Mastering Parallel Execution in OceanBase Database: Part 7 - Get Started with a PoC Test
Parallel execution is a complex subject. You need to have a proper understanding of parallel execution to make full use of its capabilities. This article aims to help you get started with parallel execution and applies to OceanBase Database V3.1 and later. Parameters in this article are not optimal but can help avoid most bad cases.
This is the last article of a seven-part series on parallel execution.
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Concurrency Control and Queuing
Part 4
Part 5
Part 6
Troubleshooting and Tuning Tips
Part 7
Initialize the Environment
Execute the following command in an analytical processing (AP) tenant:
/* MySQL */
set global parallel_servers_target = MIN_CPU * 20;
/* Oracle */
alter system set parallel_servers_target = MIN_CPU * 20;
Collect Statistics
In OceanBase Database V3.x, statistics collection is bound with major compactions. Therefore, after you import data, you must initiate a major compaction before you collect statistics.
In OceanBase Database V4.x, after you import data, you can directly call the DBMS_STAT package to collect statistics.
Set a Hint
Make sure that the maximum degree of parallelism (DOP) of an SQL statement does not exceed 1.5 times the number of physical CPU cores.
Generally, if you do not need to execute multiple SQL statements in parallel, you can set the DOP of a single SQL statement to the number of CPU cores.
For example, if the system has 32 physical CPU cores, you can set the hint as /*+ PARALLEL(32) */.
Tune the Performance
- Run the
top -Hcommand to view the CPU utilization of the current tenant. - If the performance of a single SQL statement is not as expected, contact OceanBase Technical Support to query the
sql_plan_monitorview for the performance report and contact R&D engineers for further analysis.
FAQ
- What do I do if the query performance is not as expected while the CPU resources are not fully used?
Execute the
show variables like 'parallel_servers_targetstatement and check whether the value ofparallel_servers_targetis not less than MIN_CPU × 20.
- What do I do if the PDML performance is not as expected?
Execute the EXPLAIN EXTENDED statement to verify whether parallel DML (PDML) is used. If PDML is not used, the Note field at the bottom of the plan describes the reason. Generally, if the target table contains triggers, foreign keys, or local unique indexes, PDML will not be used.
Keywords such as
DISTRIBUTED INSERT,DISTRIBUTED UPDATE, andDISTRIBUTED DELETEindicate that PDML is not used.
- What do I do when the error
-4138 OB_SNAPSHOT_DISCARDEDis returned upon a PDML timeout?
Set the undo_retention parameter to a value that is not less than the maximum execution time of a PDML statement. The default value of undo_retention is 30 minutes. If the execution time of a PDML statement exceeds 30 minutes, this error may be returned and the statement will be aborted and retried until it times out.
- How do I enable parallel execution for business SQL statements without making any modifications to the business?
OceanBase Database Proxy (ODP) provides a web UI for you to modify connection configurations to enable parallel execution. For example, you can set the DOP of all SQL statements in a read/write splitting connection to 2.
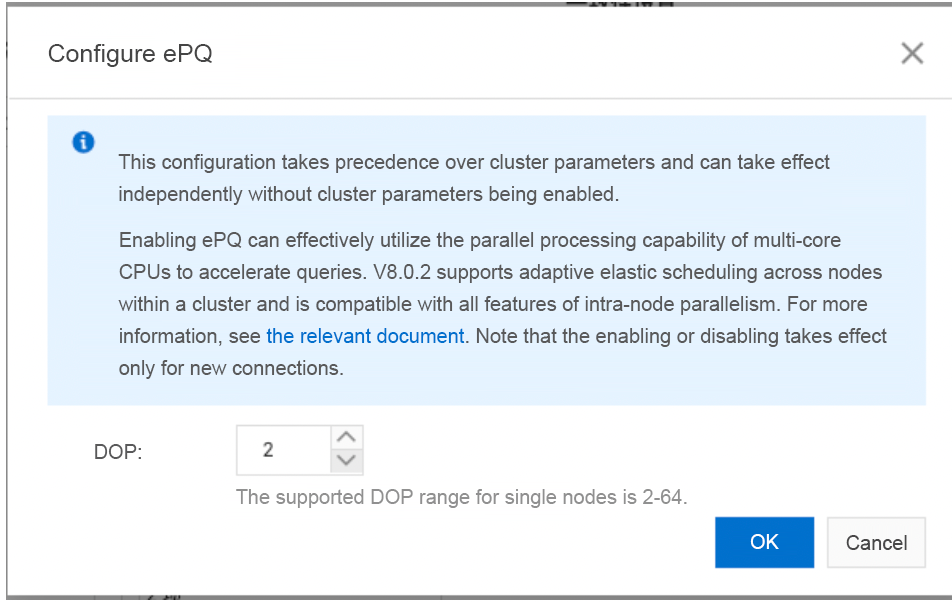
The web UI was iterated in April 2023 and released in early May 2023. Make sure that the version of ODP is V3211bp1 or later.