OpenStack: Partnering with OceanBase Database to Build a Highly Available and Scalable Infrastructure Platform
Feng Zhongyan, a senior director of the OceanBase Database community, was invited to present the joint technical solution by OceanBase Database and OpenStack at the OpenInfra Asia Summit on September 3, 2024. This article introduces the technical features and benefits of the solution in detail.
OpenStack has long been at the forefront of cloud computing, offering a powerful open source platform for building and managing cloud infrastructure. Its modular architecture enables efficient management of network resources in both public and private clouds and ensures computing and storage capabilities. Its flexibility and broad community support make it the preferred solution for enterprises seeking scalable cloud infrastructure.
As we all know, databases are essential to any software system. For OpenStack, MySQL is typically used to provide database services. As a globally renowned and widely adopted database, MySQL can run reliably and stably in most scenarios. However, as the business grows, additional solutions, such as data sharding, are often required to meet performance demands. Additionally, for OpenStack, a cloud infrastructure, high availability (HA) is crucial. Achieving HA with MySQL often requires complex configurations and external tools, such as Galera Cluster. This can incur extra complexity and O&M costs, thus affecting the overall efficiency and reliability of OpenStack.
OceanBase Database, developed by Ant Group, is a distributed relational database designed to provide cloud-native, high-performance solutions for modern large-scale applications in highly distributed environments. It offers native HA and scalability without relying on external tools or complex configurations. OceanBase Database has set world records in both TPC-C and TPC-H benchmark tests, demonstrating its exceptional performance in processing complex transactional and analytical workloads. OceanBase Database has also demonstrated its reliability, scalability, and support for mission-critical applications in real-world scenarios, providing database services to over 1,000 clients across various industries. Its cloud-native architecture ensures seamless integration with next-generation cloud platforms such as OpenStack, making it a simplified, elastic, scalable, and high-performance database solution.
Due to its cloud-native availability and scalability, OceanBase Database is an ideal choice for OpenStack. It helps reduce database O&M costs and improve the overall performance and stability of OpenStack. As cloud-native technologies become the trend in modern IT operations, deploying OpenStack and OceanBase Database on Kubernetes is a new form of building next-generation cloud infrastructure.
Integrate OceanBase Database into OpenStack for Database Services
Architecture of OpenStack
Let's first take a brief look at the architecture of OpenStack. OpenStack consists of multiple interconnected components, each responsible for different aspects of cloud infrastructure management, such as computing, storage, and networking. Each of these components has its own database to store state data, configurations, and metadata. The integrity and processing performance of these data are vital to the overall functionality and reliability of OpenStack.

Architecture of OceanBase Database
OceanBase Database is specifically designed to tackle the HA and scalability challenges of large-scale distributed systems. A typical OceanBase cluster spans three zones, with each consisting of multiple nodes for storing data replicas. OceanBase Database uses the Paxos consensus protocol to ensure data consistency across replicas. It returns a success message only after data is successfully synchronized to a majority of nodes, thus ensuring strong consistency and fault tolerance.
Additionally, OceanBase Database has introduced a multitenancy architecture for efficient data isolation and resource management. A tenant in OceanBase Database is similar to a virtual instance in MySQL. Data in a tenant is typically partitioned, with leader partitions distributed across different servers. This enables OceanBase Database to make the most of the processing capabilities of all servers, thus boosting the overall system performance.
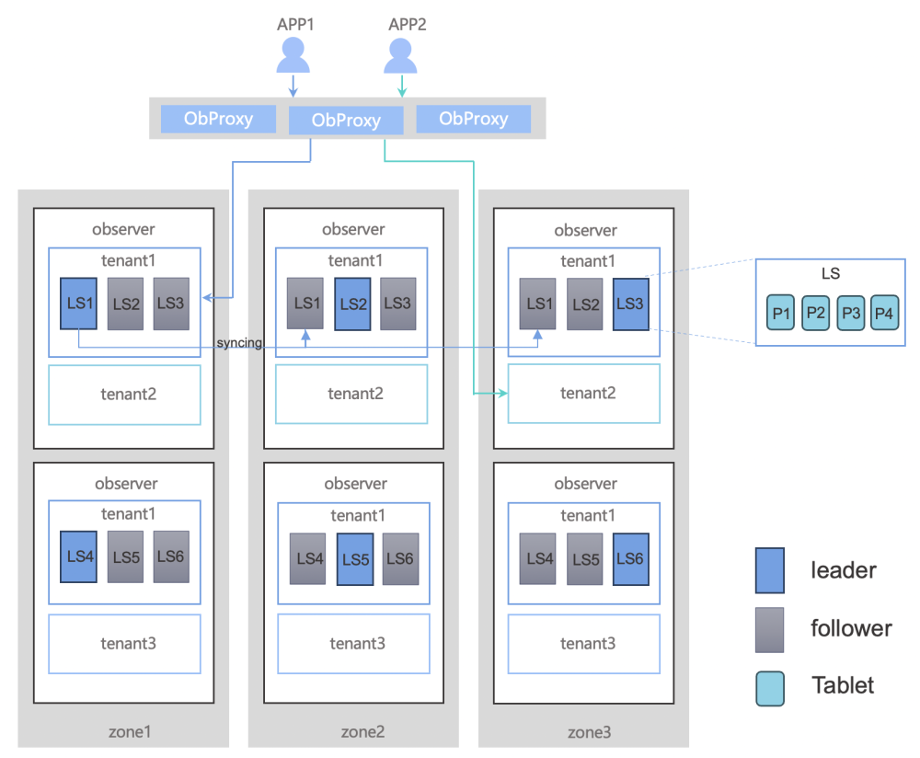
To efficiently manage and route requests in the OceanBase cluster, we have introduced OBProxy. OBProxy is a lightweight, stateless proxy server that routes requests to the most suitable OBServer nodes in the cluster. It parses SQL requests and then routes them to the leader nodes of the corresponding table partitions to ensure strong data consistency. Since OBProxy is stateless, you can easily scale it out by deploying multiple instances behind a load balancer for HA.
The preceding figure shows how OBProxy provides services in an OceanBase cluster through a load balancer. From the perspective of an application, all the components work together as one integrated system that provides database services.
OceanBase Database is compatible with the MySQL protocol, allowing you to integrate it without modifying the OpenStack code. The following figure shows the architecture where OceanBase Database is used to provide database services:
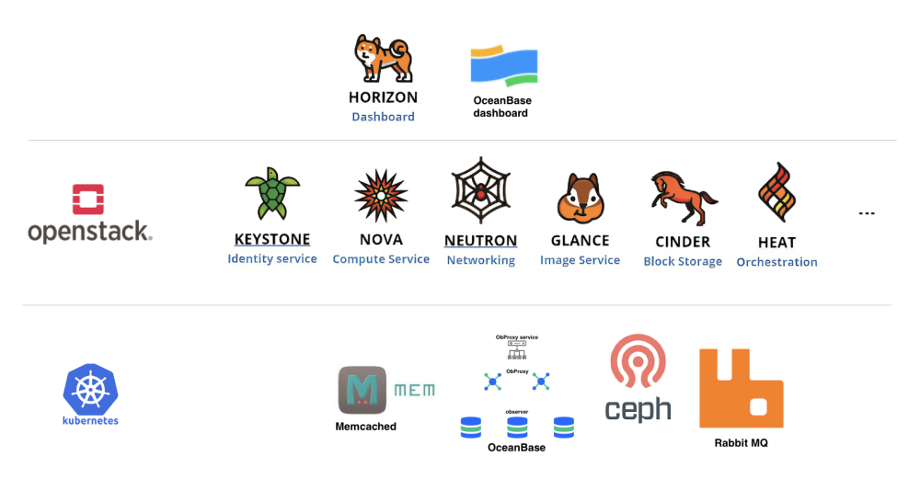
Deploy OpenStack with OceanBase Database:
To use OceanBase Database, you need to only set the database service address of each OpenStack component to the address of OceanBase Database. For example, the configurations to be updated for the Keystone component are as follows:
endpoints:
oslo_db:
auth:
admin:
username: root
password: password
keystone:
username: keystone
password: password
hosts:
default: svc-openstack
path: /keystone
scheme: mysql+pymysql
port:
mysql:
default: 2883
For most other components, only oslo_db needs to be updated. For Nova, oslo_db, oslo_db_api, and oslo_db_cell0 need to be updated. For more information, see Deploy OpenStack.
Deploy OceanBase Database:
You can easily deploy OceanBase Database on Kubernetes by using ob-operator. Only the following resources are required:
· OceanBase cluster: Define an OceanBase cluster with three zones. Each zone must consist of at least one OBServer node.
· OceanBase tenant: Define an OceanBase tenant with three replicas, which are distributed across the three zones.
· OBProxy: Deploy OBProxy with at least two instances and one service to route requests.
For more information about the configurations, see Deploy OpenStack with OceanBase on Kubernetes.
HA
Once OceanBase Database is used to provide database services for OpenStack, it equips OpenStack with HA. With its distributed architecture, OceanBase Database offers native HA, which greatly reduces operation complexity and improves reliability. OceanBase Database implements HA based on the Paxos consensus protocol, a proven approach for ensuring data consistency. Paxos requires a majority of nodes to reach a consensus on any change to the data. This enables the system to run correctly with consistent data even if some nodes fail. For example, if a node in the OceanBase cluster goes offline, Paxos ensures that the remaining nodes can process transactions without data loss. This enables OceanBase Database to tolerate hardware failures, network partitions, and other potential disruptions. OceanBase Database automatically switches the leader in the event of a failure, and OBProxy can detect this change and seamlessly route requests to the new leader. This is a fully automated process without the need for manual intervention, which ensures that applications on OceanBase Database run uninterruptedly.
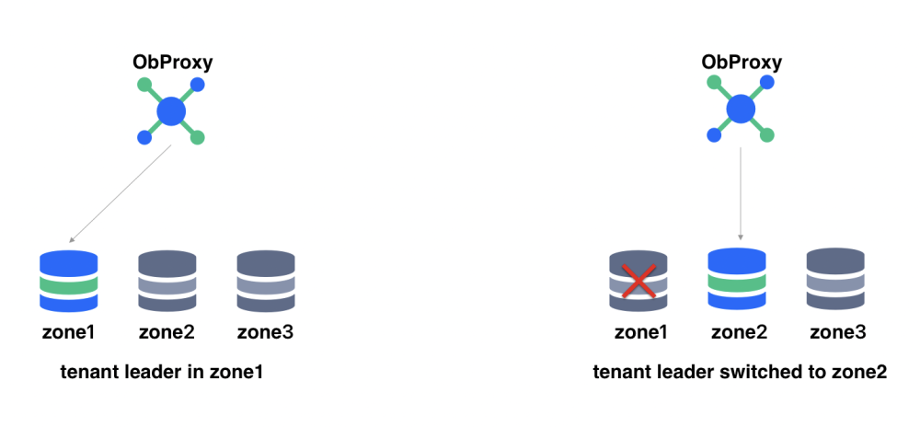
ob-operator plays an important role in the disaster recovery process of OceanBase Database. It further enhances HA, enabling OceanBase Database to provide continuous services during failures and achieve automatic disaster recovery. ob-operator maintains a fixed IP address for an OBServer node so that a new Pod can be quickly started with the same IP address in case of a Pod failure, which minimizes downtime. If the data is intact, the new Pod can be directly attached to the existing storage, allowing recovery within minutes. Even if a majority of Pods fail, OceanBase Database can recover them as long as the data is accessible.
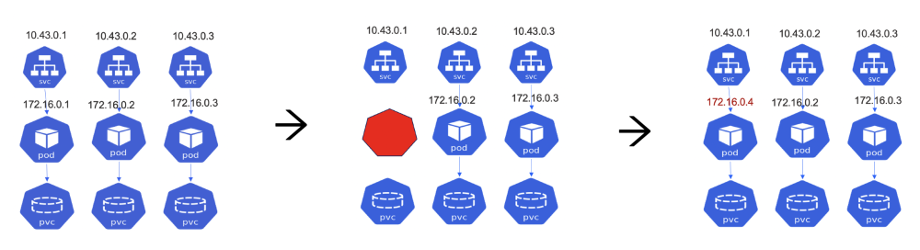
OceanBase Database offers clear benefits for OpenStack. It automatically manages node failures and ensures recovery with minimal intervention, making the infrastructure of OpenStack secure and reliable and enabling OpenStack to provide continuous services without the need for complex configurations.
For more information about other HA features such as backup, restore, and standby tenants, see High availability.
Scalability and Performance
Scalability is another core benefit of OceanBase Database which enhances the flexibility of OpenStack. Unlike conventional databases, OceanBase Database does not become a bottleneck of the system in the event of heavy loads because its distributed architecture can be easily scaled out. By adding more nodes to the cluster, you can seamlessly increase the processing capability and storage capacity of OceanBase Database.
OceanBase Database achieves dynamic scaling through several strategies. It stores data by partition to effectively prevent a single node from becoming a bottleneck. When new nodes are added to the cluster, OceanBase Database automatically balances loads and migrates data to maximize the system performance.
OceanBase Database supports real-time dynamic adjustment of CPU, memory, and storage resources for tenants, enabling quick response to frequent load changes. This feature is crucial in cloud environments, allowing administrators to quickly adjust resources based on loads at any time.
Scaling out an OceanBase cluster is easy. Assume that an OceanBase cluster has three zones and each zone has one OBServer node. When loads increase, the administrator can scale out the cluster to two OBServer nodes per zone by modifying the replica information of each zone defined in the cluster resource specification.
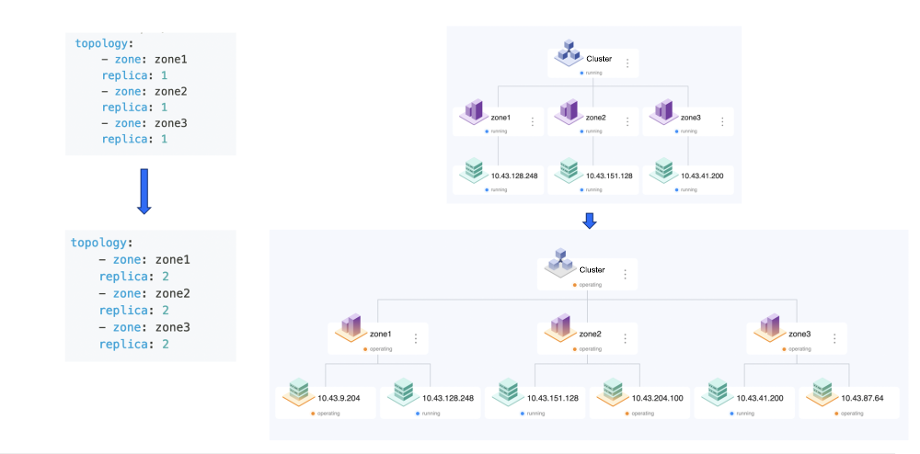
After adding the OBServer nodes, the administrator needs to only change the unitNum value to 2 to double the processing capability.
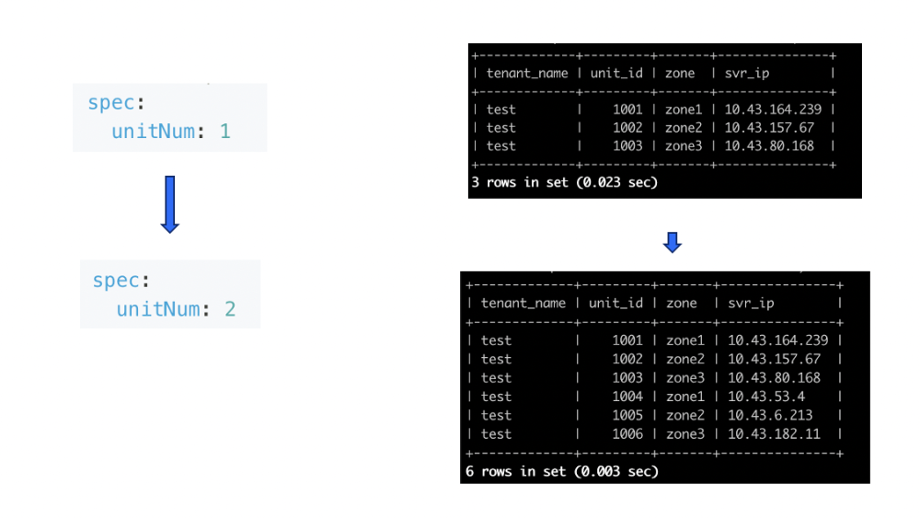
The scalability of OceanBase Database empowers OpenStack to effortlessly support large-scale applications and fast-growing businesses, making it an ideal database solution for OpenStack.
For more information about the scalability of OceanBase Database, including tenant management and dynamic resource adjustment, see Manage tenants.
Conclusion
OceanBase Database is a highly available and scalable database solution for OpenStack. Its cloud-native architecture, native HA, and seamless scalability align perfectly with modern cloud infrastructures. The next-generation solution of integrating OceanBase Database as the database layer into OpenStack helps tackle the scale, flexibility, and stability challenges in cloud-based scenarios. With this solution, cloud vendors can greatly enhance resilience and performance, reduce the O&M complexity, and improve the service reliability of their cloud environments.
As demonstrated earlier, deploying OceanBase Database in an OpenStack environment in just a few simple steps brings obvious benefits in HA and scalability. As cloud-native technologies evolve, the integration of OceanBase Database with OpenStack and Kubernetes provides an innovative way to build powerful, scalable, and resilient cloud infrastructure. For enterprises aiming to improve and adapt their IT operations for the future, OceanBase Database is a powerful and easy-to-implement solution that enhances the key features of OpenStack, making it a significant force in the cloud computing field.