Sunshine Insurance`s Business System Has Run on OceanBase Database Stably for over 700 Days
Che Dongxing: Currently employed at Sunshine Insurance, Che has been working in the IT field within the insurance industry for 12 years, and has acquired profound knowledge of IT infrastructure practices in this industry. Also, he is familiar with various database products, and has great experience in database O&M.
Wang Huacheng: Currently employed at Sunshine Insurance, Wang has engaged in MySQL database O&M for more than 10 years, and has gained rich experience in the O&M of on-premise and cloud databases. In recent years, he has conducted comprehensive research on MySQL-compatible databases.
Background
Founded in July 2005, Sunshine Insurance Group is one of the fastest-growing market-oriented enterprises in the world. It is now among the top eight in China's insurance industry, with a number of subsidiaries specialized in a range of fields, such as property insurance, life insurance, credit guarantee insurance, and asset management. Facing the booming trend of digital upgrade, many enterprises need to upgrade their software and hardware to meet the requirements of independent R&D. Databases, one of the three pillars of software, are no exception.
Against the backdrop of digital upgrade, Sunshine Insurance Group began working on database selection and upgrade according to our own business requirements. To begin with, we learned about distributed databases to get prepared for future business growth. Next, we thoroughly investigated and tested several products in line with the principle that the database system must meet our business requirements with minimal software and hardware costs.
At last, we settled on OceanBase Database for four reasons:
First, it ticks all key boxes for our business upgrade. OceanBase Database is a distributed database developed fully in house and its core source code was opened to the community in 2021.
Second, it is stable and reliable. The whole system has been running stably for more than 2 years with zero data loss. We have trust in it. Technically, OceanBase Database supports multi-replica disaster recovery based on the Paxos protocol. The database provides high availability with a recovery point objective (RPO) of 0 and a recovery time objective (RTO) of less than 8s when a minority of replicas fail. From the business point of view, OceanBase Database has empowered the Double 11 shopping festival for more than a decade, and has been polished up by the core systems of many financial organizations, delivering proven performance and reliability.
Third, it is highly compatible with MySQL. Compatibility was our main concern, because many of our business systems were built on MySQL infrastructure. Insufficient compatibility not only results in high migration and reconstruction costs, but also requires exhausting business modifications. Therefore, the new technologies or new products must ensure seamless and smooth migration with minimal reconstruction costs.
Fourth, it features multitenancy. We had deployed multiple MySQL instances to support our various business systems, which caused significant strain with heavy O&M workload despite the medium business traffic and data volume. The native multitenancy feature of OceanBase Database solves this problem and significantly simplifies our O&M work.
Benefits
After a break-in period, we have gradually migrated our existing business systems to OceanBase Database. Our online environment was based mainly on MySQL 5.6 and 5.7. Using OceanBase Migration Service (OMS), a dedicated data migration tool, we easily created synchronization tasks that automatically migrated data from MySQL instances to OceanBase Database without any compatibility issues. The whole migration process was quite smooth, saving a large amount of implicit migration costs.
We have deployed OceanBase Database V3.1.5 on a single server with 128 CPU cores and 768 GB of memory, and created 22 tenants to host business modules migrated from original MySQL instances. This way, each business module uses exclusive tenant resources without affecting each other. The new solution also achieves high availability and simplifies O&M management.
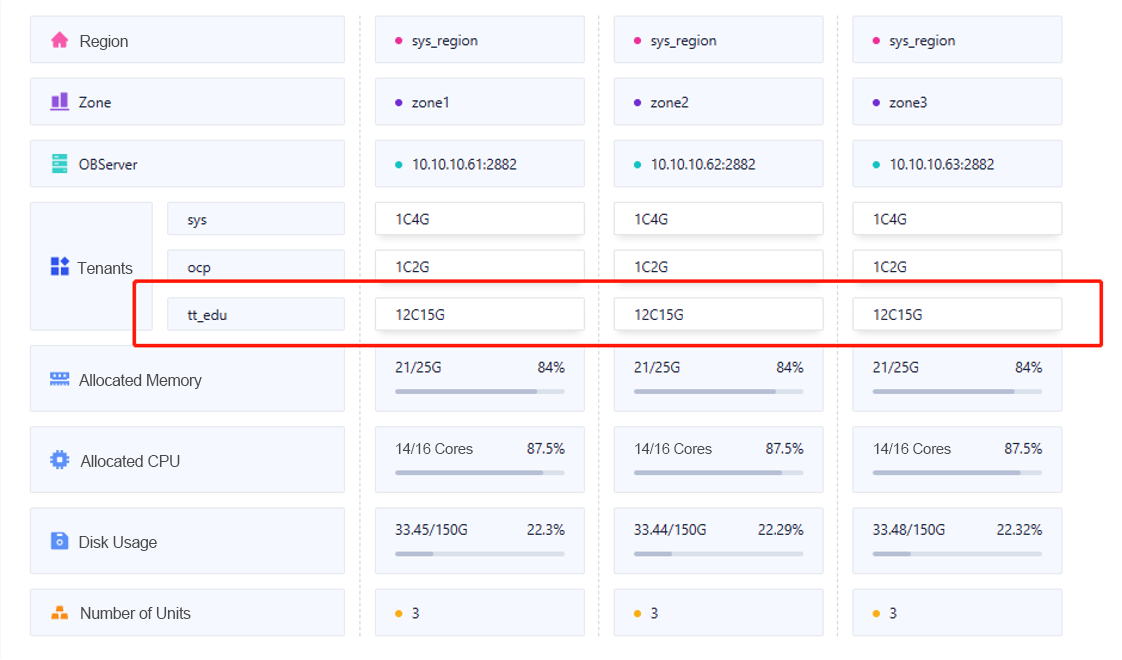
I. Multitenancy and Resource Isolation to Improve Resource Utilization and Ensure Data Security
The multitenancy feature of OceanBase Database simplifies the O&M of MySQL instances that host many small business modules. A tenant is a logical unit designed for resource isolation. The data security of tenants is guaranteed by privilege control. Tenants are critical for system O&M, especially for the O&M of cloud databases. In a sense, tenants are comparable to "instances" in a conventional database system. In OceanBase Database, tenants are totally isolated, which prevents cross-tenant access and ensures that data assets of a tenant cannot be used by other tenants. Therefore, we can migrate our business modules hosted in multiple MySQL instances to different tenants of one OceanBase cluster, without worrying about data security. In addition, resources are allocated based on tenants. We can allocate resources according to our business needs, making the most out of server resources. The following figure shows our resource allocation for tenants.
II. Intervention-free Stable Operation with Zero Data Loss Guaranteed by High Availability
Our original MySQL architecture consisted of a master node and several slave nodes, and lacked high availability. Therefore, we were highly concerned about its stability in some complex, large-scale business scenarios. When the master node hosting the core business was abnormal or down, manual intervention, such as manual master/slave switchover and data replenishment based on binlogs, might be required to deal with the problem. This workaround, while solving the problem, was risky and inconvenient. OceanBase Database supports multi-replica disaster recovery based on the Paxos protocol. Our three-replica solution provides high availability with an RPO of 0 and an RTO of less than 8s when one replica fails, ensuring that our upper-layer business remains unaffected in this scenario.
III. Diverse Ecosystem and Easy O&M
The work efficiency of database administrators (DBAs) relies largely on whether their database O&M tools are easy to use. OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) is an O&M tool that provides a series of GUI-based management features for OceanBase Database and related resources, such as full-lifecycle management, monitoring and alerting, performance diagnostics, fault recovery, and backup and restore. OCP allows us to efficiently manage OceanBase Database, thereby reducing our IT O&M costs and learning costs. For us, three features are worth mentioning.
First, an overview of database basics and cluster performance is provided on a graphical page. Database O&M engineers often need to locate and handle slow SQL statements. OCP allows them to view top SQL statements that consume most system resources and slow SQL statements on graphical pages, which also quickly display the required information.
Second, scaling is easier. To add a slave node to our MySQL environment, we must modify many parameters, and might need to restart the service. With the help of OCP, we only need to simply configure a tenant for online scaling without business interruptions.
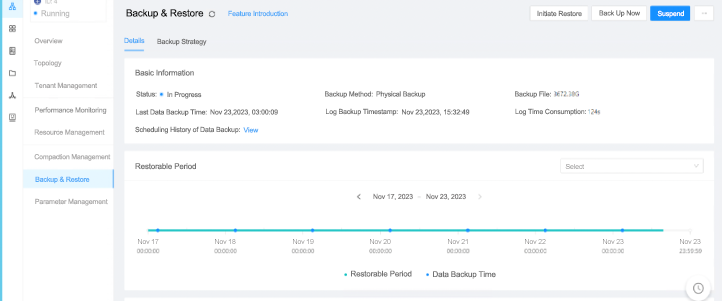
Third, restoring data from backups is more convenient. In our original MySQL database, we could restore the data to a specified point in time, but the procedure was troublesome. We needed to find the corresponding binlog files, and then specify the files to be parsed and the target point in time in the commands. In the GUI-based OCP console, we only need to specify the target point in time.
We also tried other data management platforms. Most of them, from our point of view, provide few features and are complex to use. OCP, on the contrary, provides various features and great user experience.
Practical Experience
OceanBase Database has brought significant benefits to us. However, we would like to point out something noteworthy based on our experience.
- The use of an auto-increment column: In MySQL, an auto-increment column automatically generates unique, incremental values to uniquely identify the data of the corresponding rows. In OceanBase Database V3.1.x, the values of an auto-increment column may hop and therefore are not consecutive. This is because, unlike centralized databases such as MySQL, OceanBase Database features a distributed architecture where data replicas are located across different servers. To ensure high compatibility with MySQL while maintaining the performance of auto-increment column value generation in a distributed system, the issue of value hopping may occur. However, as long as the values of the auto-increment column are unique, value hopping has limited impact on our business.
- An issue of direct upgrade: We have deployed OceanBase Database V3.1.5, which cannot be directly upgraded to V4.x. Data migration and synchronization are required when switching the environment, much like the upgrade process of Oracle Database of earlier versions.
Afterword
Our production system has been stably running on an OceanBase cluster for two years. We have learned that OceanBase Database V4.x provides more powerful online analytical processing (OLAP) and data compression capabilities, and its compatibility with MySQL is also improved greatly. Therefore, we plan to migrate our data-intensive business modules to OceanBase Database V4.x to further reduce our hardware costs. We will also migrate more business modules to OceanBase Database according to our key business upgrade requirements.