Node Failures
Business and Database Symptoms
Business symptom: Business fails.
Database symptom: Database services held by a certain OBServer node are unavailable.
Troubleshooting Approach and Procedure
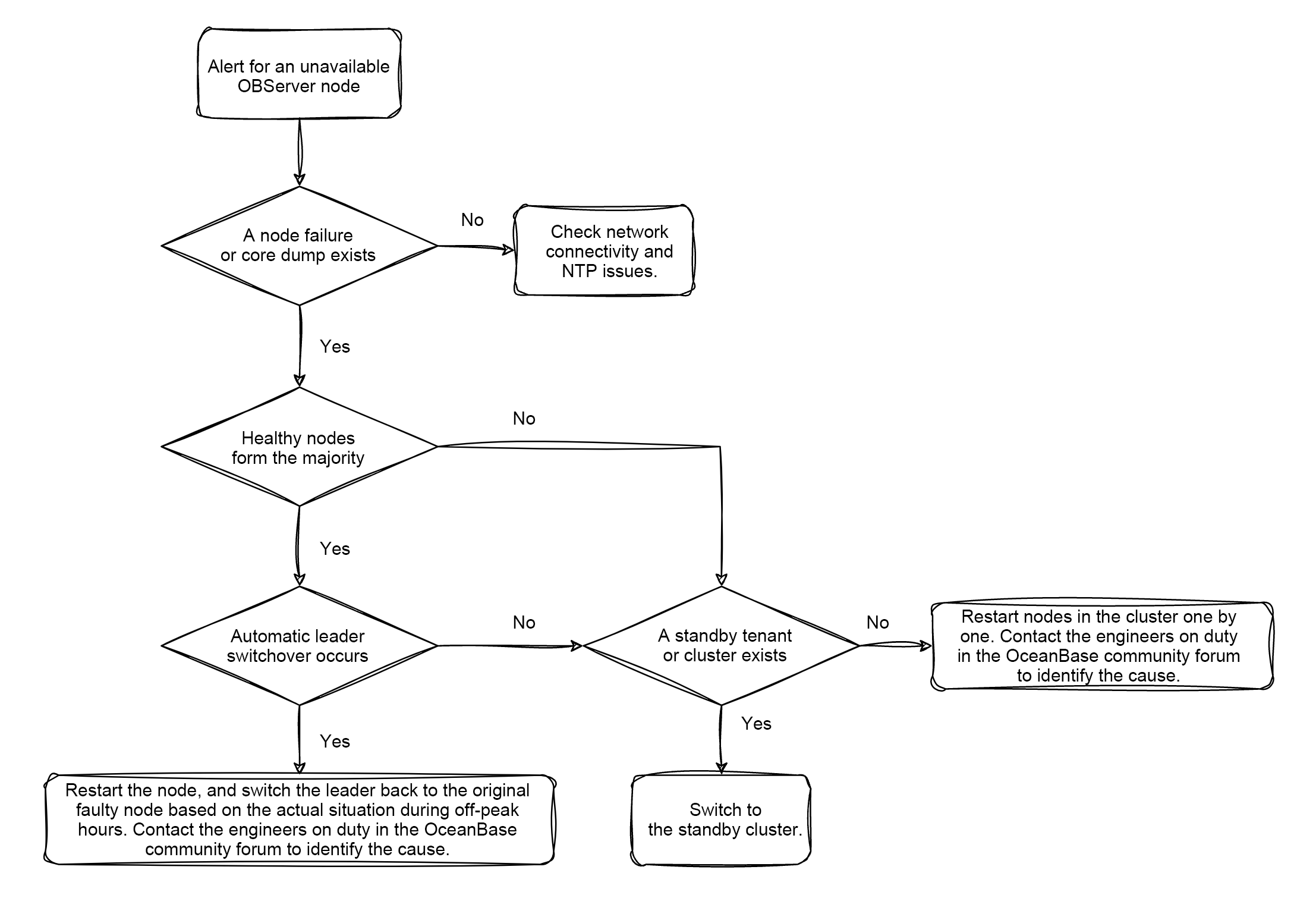
Troubleshoot node failures
Check the availability of the host. If you can log in to the node, run the ps command to check whether the observer process is running on the node.
$ps -ef | grep observer
03:55:52 /home/xiaofeng.lby/obn.obs0/bin/observer
00:00:00 grep --color=auto observer
If the observer process is running on the node, test the network connectivity of the host on which the node resides. This aims to identify misreported alerts due to network isolation between nodes and network jitter.
For more information, see Troubleshoot NTP clock synchronization issues.
If healthy nodes cannot form the majority
If the host or network issue cannot be fixed in time, try the following measures in order:
-
Initiate a failover to switch the physical standby tenant or cluster to the primary role in OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP).
-
Use the physical backup and restore feature in OCP.
-
If no physical standby database or data backup is available, restart the observer process on each node in the cluster, one by one.
-
If the issue persists after the restart, contact the engineers on duty in the OceanBase community forum for troubleshooting.
-
Contact the engineers on duty in the OceanBase community forum to identify the cause.
We recommend that you back up important data and key tenants in the production environment to prevent losses caused by unexpected faults. You can use the physical backup and restore feature and create standby tenants or clusters in the OCP console.
If healthy nodes can form the majority
-
If healthy nodes in the cluster can form the majority, the cluster can elect a new leader within eight seconds by using its high-availability capability and continue to provide services. You need to only restart or replace the abnormal nodes. In most cases, the issue is fixed after you perform the preceding operations. You can record the following statements.
-- Before a fault occurs
SELECT SVR_IP, ROLE, SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN)
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_LOG_STAT
WHERE TENANT_ID = 1 order by LS_ID, ROLE;
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+
| SVR_IP | ROLE | SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN) |
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+
| xx.xxx.xxx.1 | FOLLOWER | 2024-11-27 19:44:27.881516 |
| xx.xxx.xxx.2 | FOLLOWER | 2024-11-27 19:44:27.881516 |
| xx.xxx.xxx.3 | LEADER | 2024-11-27 19:44:27.881516 |
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+
-- After the system elects the leader
SELECT SVR_IP, ROLE, SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN)
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_LOG_STAT
WHERE TENANT_ID = 1 order by LS_ID, ROLE;
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+
| SVR_IP | ROLE | SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN) |
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+
| xx.xxx.xxx.1 | FOLLOWER | 2024-11-27 19:44:38.737837 |
| xx.xxx.xxx.2 | LEADER | 2024-11-27 19:44:38.737837 |
+---------------+----------+----------------------------+The
SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN)function obtains the latest system change numbers (SCNs) of replicas of a specific log stream and converts them into timestamps. If the difference between the latest SCN of followers and that of the leader is within five seconds, the logs have been synchronized. -
If the cluster cannot provide services, isolate the abnormal nodes first. Then, determine whether to specify a greater value for the server_permanent_offline_time parameter. By default, this parameter is set to one hour.
-- Check the status of nodes in the cluster.
select SVR_IP, SVR_PORT, ZONE, WITH_ROOTSERVER, STATUS from oceanbase.DBA_OB_SERVERS;
+---------------+----------+-------+-----------------+----------+
| SVR_IP | SVR_PORT | ZONE | WITH_ROOTSERVER | STATUS |
+---------------+----------+-------+-----------------+----------+
| xx.xxx.xxx.3 | 2882 | zone3 | NO | INACTIVE |
| xx.xxx.xxx.2 | 2882 | zone2 | YES | ACTIVE |
| xx.xxx.xxx.1 | 2882 | zone1 | NO | ACTIVE |
+---------------+----------+-------+-----------------+----------+
-- Check the value of the server_permanent_offline_time parameter.
show parameters like "%server_permanent_offline_time%";
-- Stop the abnormal node to isolate it.
alter system stop server 'xx.xxx.xxx.3:2882';STOP SERVERis the most secure statement for node isolation. TheSTOP SERVERstatement can switch the business traffic from an abnormal node to isolate the node from the business traffic. The statement can also ensure that other nodes are still the majority in the Paxos group. This way, you can securely perform all actions on the isolated node. For example, you can run thepstackorobstackcommand, adjust the log level, or even stop the observer process. When you need to isolate a fault or stop a node for maintenance, you can use theSTOP SERVERstatement, which is the best choice in this case. -
If the cluster remains faulty two minutes after you execute the previous step, manually specify a zone with no faulty nodes as the primary zone for the leader switchover.
ALTER TENANT tenant_name primary_zone='zone1';
-- Check the ROLE column in the GV$OB_LOG_STAT view to determine whether the leader switchover is successful.
SELECT SVR_IP, ROLE, SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN)
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_LOG_STAT
WHERE TENANT_ID = 1 order by LS_ID, ROLE; -
If the cluster still cannot provide services three minutes after the leader switchover, refer to the "If healthy nodes cannot form the majority" section of this topic.
-
Contact the engineers on duty in the OceanBase community forum to identify the cause.
References
Updates Released on December 4, 2024
I want to provide more suggestions for you.
-
If the host of the node can be restored, you can restart the node in OCP.
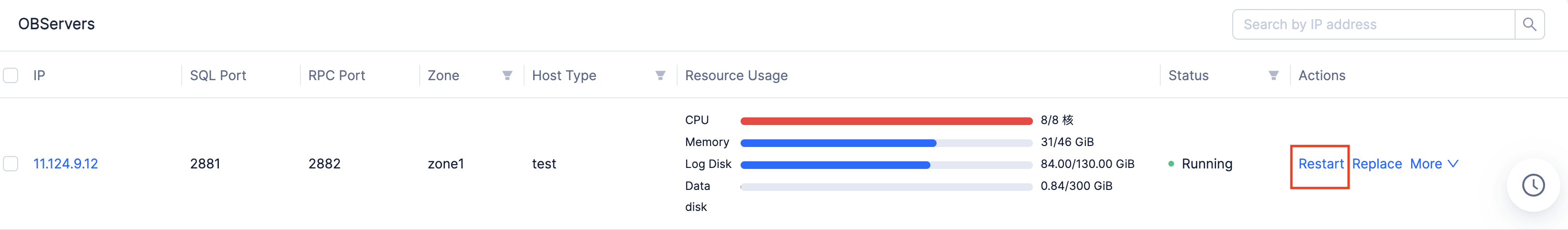
If the node cannot be immediately restarted in OCP, you can go to the installation directory of the node and manually start its observer process.
[xiaofeng.lby@sqaobnoxdn011161204091.sa128 /home/xiaofeng.lby/oceanbase]
$sudo su admin
[admin@sqaobnoxdn011161204091.sa128 /home/xiaofeng.lby/oceanbase]
$export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/xiaofeng.lby/oceanbase/lib
[admin@sqaobnoxdn011161204091.sa128 /home/xiaofeng.lby/oceanbase]
$./bin/observer
./bin/observerNote that you must run the
./bin/observercommand in the/oceanbasedirectory. This may be because specific configuration files in theetcdirectory are required.[admin@sqaobnoxdn011161204091.sa128 /home/xiaofeng.lby/oceanbase]
$find . -name observer.config.bin
./etc/observer.config.bin -
After you restart the node, you can switch back to the original leader during off-peak hours. This prevents the session from accessing the leader through cross-IDC communication for a long period of time.
ALTER TENANT tenant_name primary_zone='zone1';
-- Check the ROLE column in the GV$OB_LOG_STAT view to determine whether the leader switchover is successful.
SELECT SVR_IP, ROLE, SCN_TO_TIMESTAMP(END_SCN)
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_LOG_STAT
WHERE TENANT_ID = 1 order by LS_ID, ROLE; -
If the host of the node cannot be restored, add a new node to replace the abnormal node in OCP. After the new node is added, the system automatically adds replicas.
-
If no new host is available, you can temporarily use two replicas to provide services. However, this method does not ensure high availability and may cause risks. You must put new hosts online at the earliest opportunity.