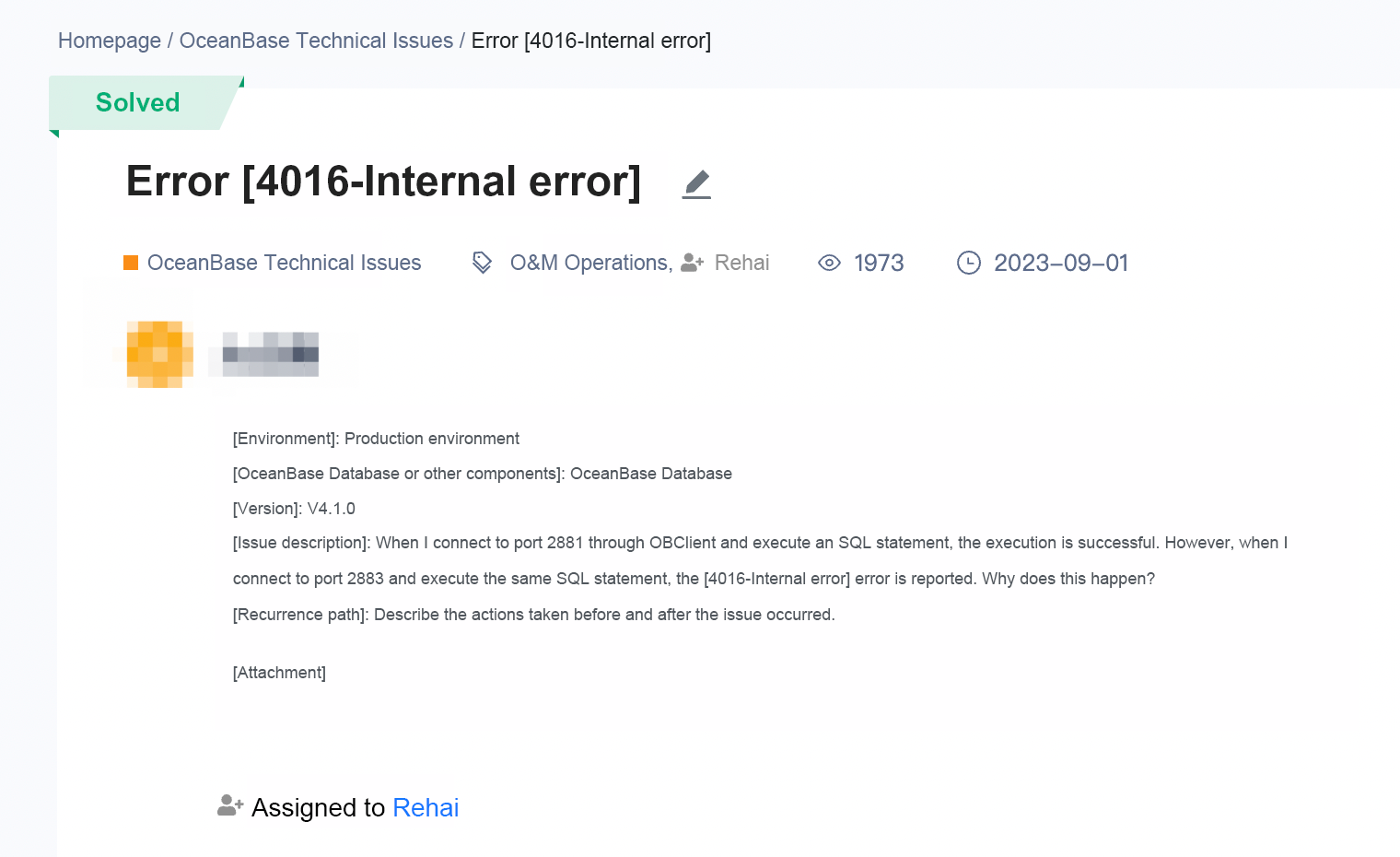
Unexpected Errors
Background Information
Many of you may submit questions to the OceanBase community forum when you encounter unexpected errors.
However, it is often observed that only the error code is included in the questions, which is insufficient. You need to include more relevant information, such as the OceanBase Database version, the SQL statement involved, and logs. This helps engineers on duty reproduce the error and identify its cause.
In the following example, only an error code that indicates an internal error is provided, which does not help identify the error cause. The user must also provide relevant logs.
This topic describes the information that you need to provide to the engineers on duty in the community forum when you encounter unexpected errors, as well as how to retrieve logs.
Required Information
The information that you provide will be used by OceanBase Technical Support engineers to reproduce the error and identify its cause. In most cases, the following information is required:
- The table schema involved in the error
- The SQL statement that triggered the error
- The logs that correspond to the error
Retrieve Logs
For example, an error is reported when I create a database named zlatan_db in a special version of OceanBase Database.
obclient> create database zlatan_db;
ERROR 4016 (HY000): Internal error
I can use one of the following methods to retrieve corresponding logs.
Method 1: select last_trace_id()
In the same session, execute the select last_trace_id() statement after the SQL statement that triggered the error.
obclient> create database zlatan_db;
ERROR 4016 (HY000): Internal error
obclient> select last_trace_id();
+------------------------------------+
| last_trace_id() |
+------------------------------------+
| Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0 |
+------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Then, run a grep command in a log directory similar to /home/user_name/oceanbase/log to search for the occurrences of the trace ID in log files.
If the directory contains a small number of log files, run the grep trace_id * command in the directory.
grep Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0 * > zlatan.log
Otherwise, run a grep command to search for the occurrences of the trace ID in log files generated within a specific period of time.
grep Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0 observer.log.2024121918* rootservice.log.2024121918* > zlatan.log
Upload the zlatan.log file as an attachment to the question and then post the question in the forum.
You can also highlight ret=-4016 in the zlatan.log file, as the reported error code is 4016. The direct cause of the error is found next to the first occurrence of ret=-4016 in the logs.
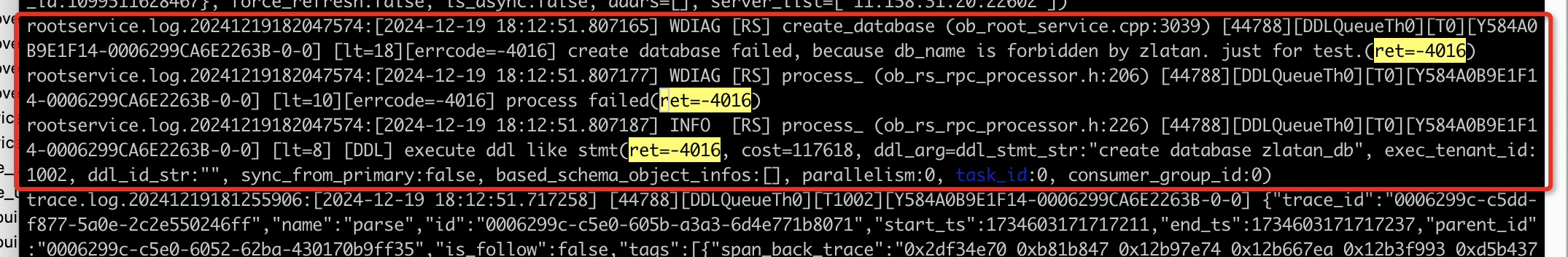
rootservice.log.20241219182047574:[2024-12-19 18:12:51.807165] WDIAG [RS]
create_database (ob_root_service.cpp:3039) [44788][DDLQueueTh0][T0]
[Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0] [lt=18][errcode=-4016]
create database failed, because db_name is forbidden by zlatan. just for test.(ret=-4016)
rootservice.log.20241219182047574:[2024-12-19 18:12:51.807177] WDIAG [RS] process_
(ob_rs_rpc_processor.h:206) [44788][DDLQueueTh0][T0]
[Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0] [lt=10][errcode=-4016] process failed(ret=-4016)
rootservice.log.20241219182047574:[2024-12-19 18:12:51.807187] INFO [RS]
process_ (ob_rs_rpc_processor.h:226) [44788][DDLQueueTh0][T0]
[Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0] [lt=8] [DDL]
execute ddl like stmt(
ret=-4016, cost=117618, ddl_arg=ddl_stmt_str:"create database zlatan_db",
exec_tenant_id:1002, ddl_id_str:"", sync_from_primary:false,
based_schema_object_infos:[], parallelism:0, task_id:0, consumer_group_id:0)
The preceding results show that the direct cause of error 4016 is create database failed, because db_name is forbidden by zlatan. just for test.
This is because I modified the code in this special version of OceanBase Database to prevent users from naming a database zlatan_db. You will never encounter the error. Don't worry.
int ObRootService::create_database(
const ObCreateDatabaseArg &arg,
UInt64 &db_id)
{
int ret = OB_SUCCESS;
// other codes, we ignore
// ...
// add by zlatan, just for debug
ObString forbidden_db_name = "zlatan_db";
if (arg.database_schema_.get_database_name_str() == forbidden_db_name) {
ret = OB_ERR_UNEXPECTED;
LOG_WARN("create database failed, because db_name is forbidden by zlatan. just for test.", K(ret));
}
return ret;
}
Method 2: grep "ret=-errno"�
Method 1 is limited, as you must execute the select last_trace_id() statement immediately after the SQL statement that triggered the error, within the same session.
If another SQL statement has been executed after the SQL statement that triggered the error or the session is exited, you can run the grep "ret=-errno" command to obtain the trace ID.
$grep "ret=-4016" *
observer.log.20241219181453955:[2024-12-19 18:12:51.807313]
WDIAG [RPC] send (ob_poc_rpc_proxy.h:176) [46486][T1002_L0_G0][T1002]
[Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0] [lt=10][errcode=-4016]
execute rpc fail(addr="11.158.31.20:22602", pcode=520, ret=-4016, timeout=999999400)
...
Then, retrieve complete logs by running a grep command with the trace ID, which is Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0 in this example.
grep Y584A0B9E1F14-0006299CA6E2263B-0-0 * > zlatan.log
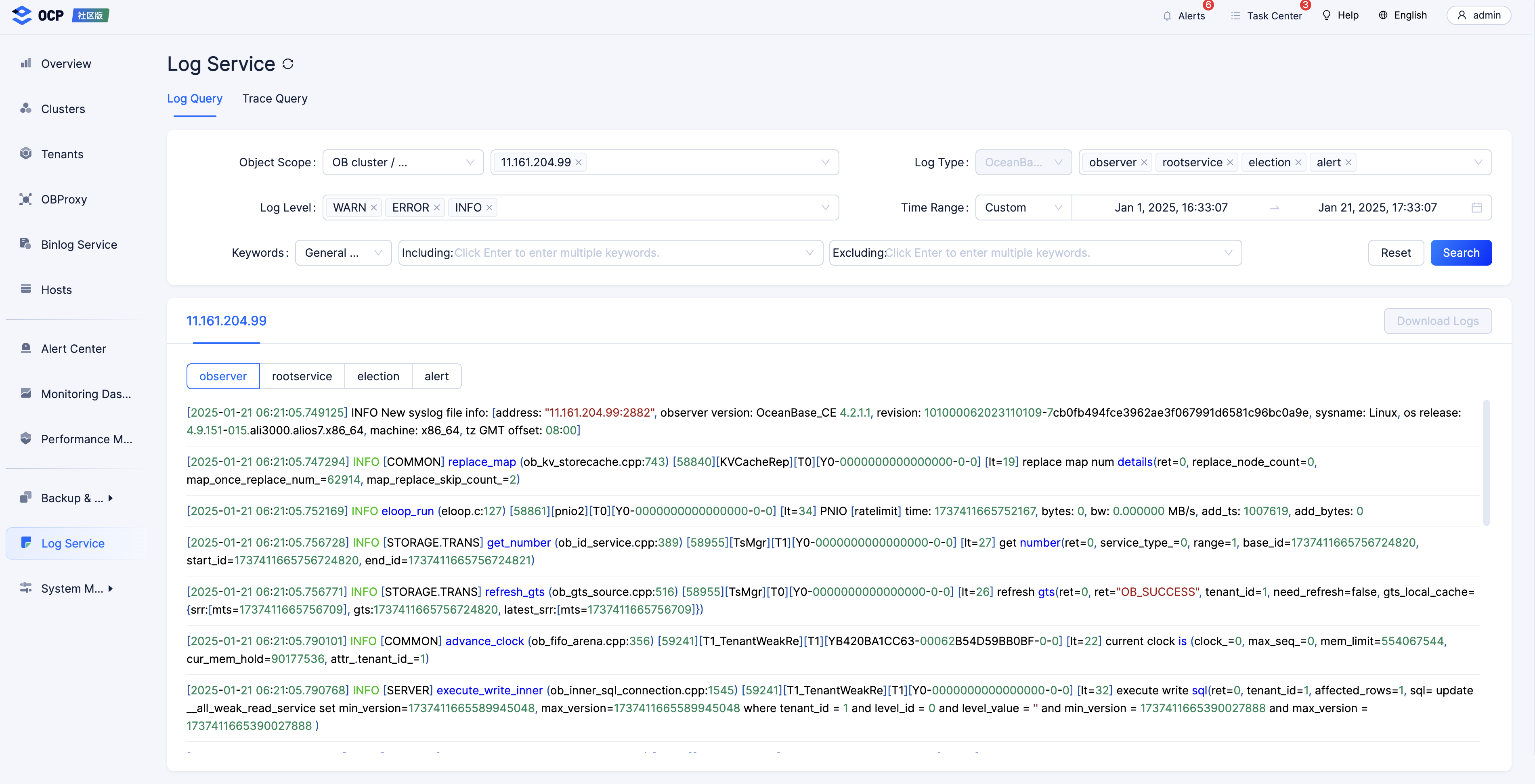
Method 3: logs from OCP
If you do not want to run a grep command to retrieve logs, you can perform GUI-based operations to obtain logs from OCP. You can use the keyword ret=-errno to obtain the logs within the specified time range.
What to Do Next
Submit your question in the community forum, with the logs attached.