OMS Community Edition Troubleshooting Guide
Why do we provide a troubleshooting manual for OMS Community Edition?
On the one hand, most documentation on the official website of OceanBase Database is intended for the Enterprise Edition, but the Enterprise Edition and Community Edition of OceanBase Migration Service (OMS) are totally independent of each other. Therefore, a troubleshooting manual for users of the Community Edition is required.
On the other hand, lightweight O&M tools such as OceanBase Deployer (obd) are dedicated for OceanBase Database Community Edition, and will be supported for OceanBase Database Enterprise Edition later. However, a detailed obd troubleshooting manual is absent on the official website.
As for tools like OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) whose Enterprise Edition and Community Edition are built based on the same set of code, you can visit the official website for the troubleshooting information.
This troubleshooting manual is written personally by Liu Che, the R&D director of OMS Community Edition, and is a valuable reference for troubleshooting OMS. Feel free to read through this manual and save it as a favorite.
Today I chatted with Xie Yun, the R&D director of obd. He said that many users of OceanBase Database Community Edition are using obd for O&M management of clusters. A similar troubleshooting manual for obd Community Edition will be released in December 2024.
Troubleshooting Procedure
When an error occurs in OMS Community Edition, check whether the error is caused by the limitations mentioned in the official documentation.
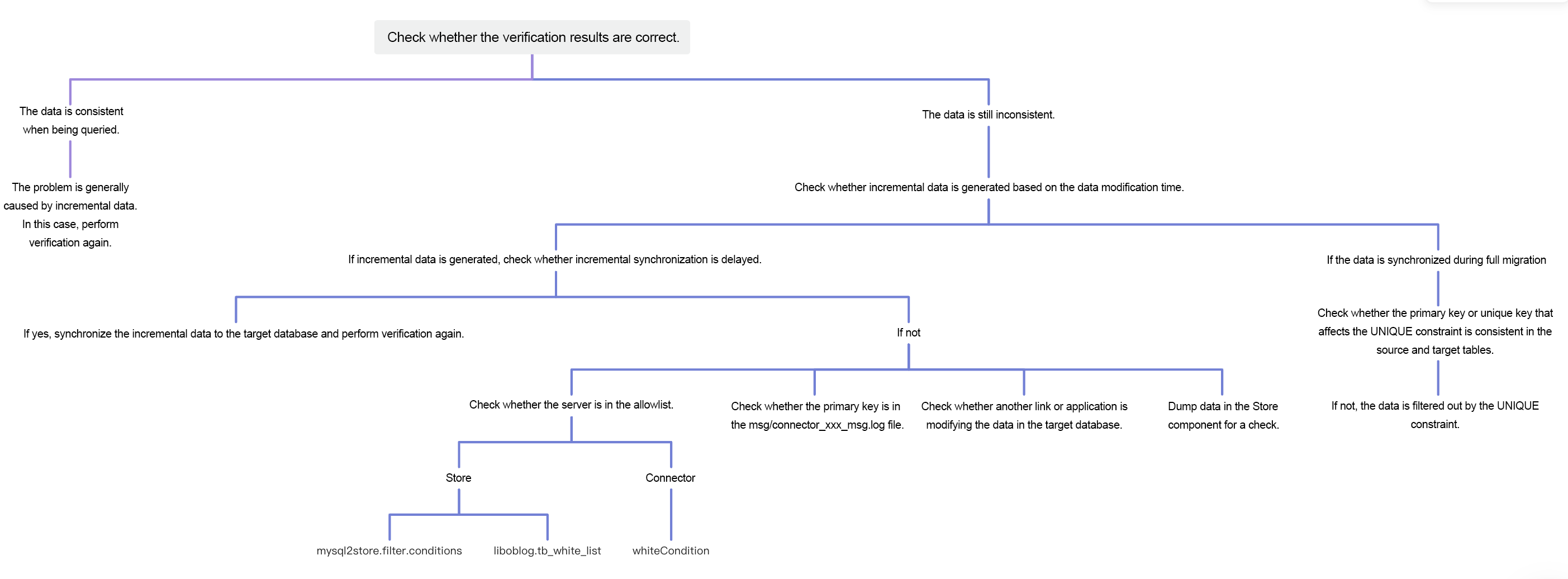
The following figure shows the overall troubleshooting procedure when an error occurs in a data migration or synchronization task in OMS Community Edition.
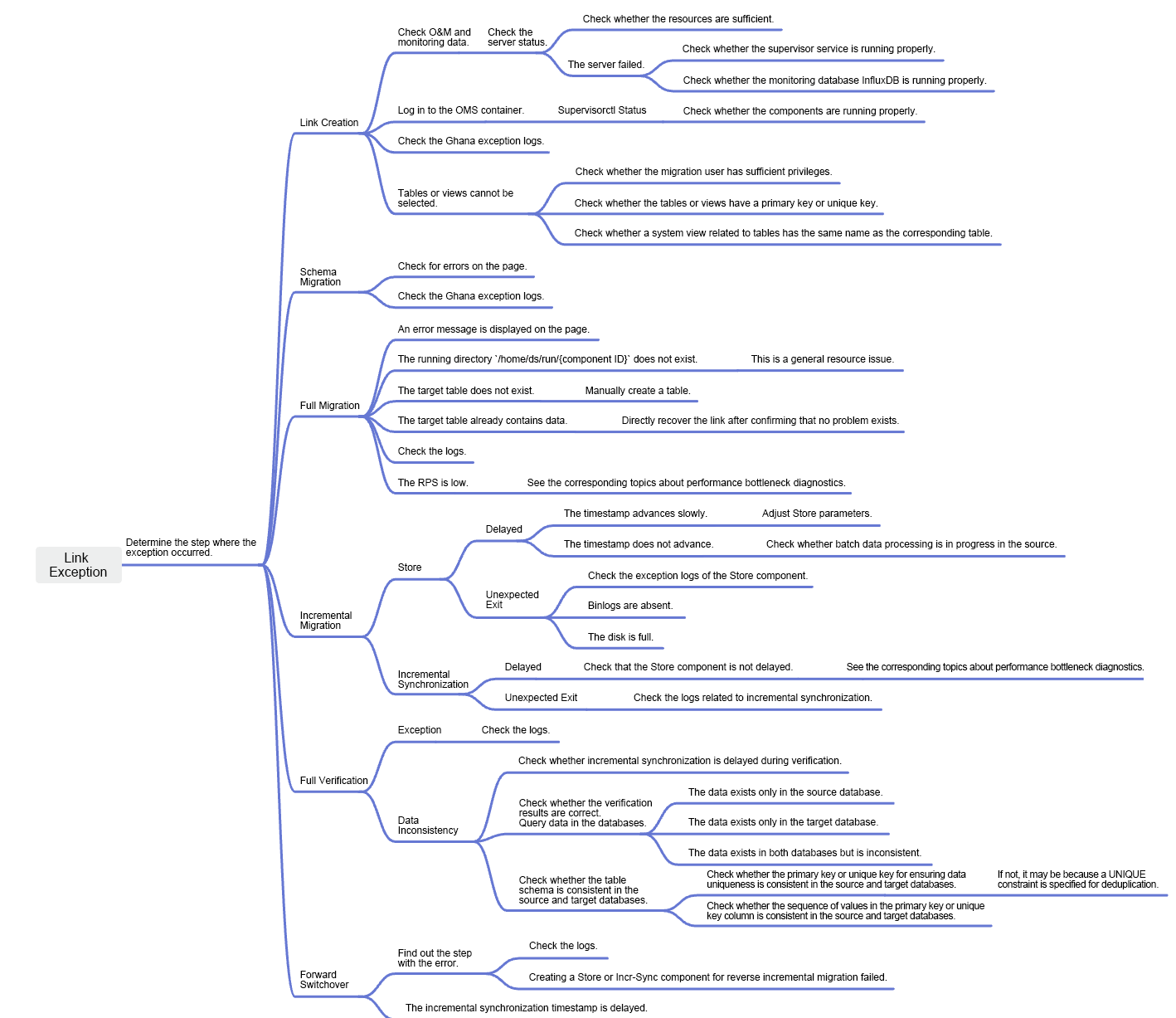
Features, Components, and Log Locations
Note:
All log files are automatically archived and compressed. If you want to view logs, locate the log file by time.
Schema migration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Ghana |
| Log directory | /home/admin/logs/ghana/Ghana |
| Schema conversion logs | dbcat.log |
| Common error logs | common-error.log |
| Common output logs | common-default.log |
| Query logs | check_query.log |
| Task logs | oms-step.log |
| Background scheduling logs | oms-scheduler.log |
Full migration
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Connector |
| Log directory | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/logs |
| Error logs | error.log |
| Operation logs | connector.log |
Perform the following steps to query the component ID:
-
Log in to the console of OMS Community Edition.
-
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Migration.
-
On the Data Migration page, click the name of the target data migration task to go to its details page.
-
Click View Component Monitoring in the upper-right corner.
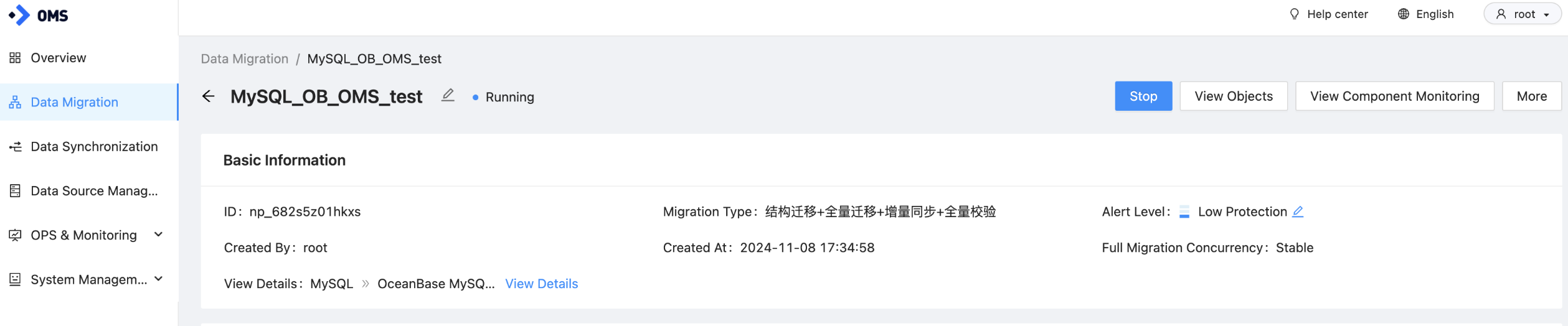
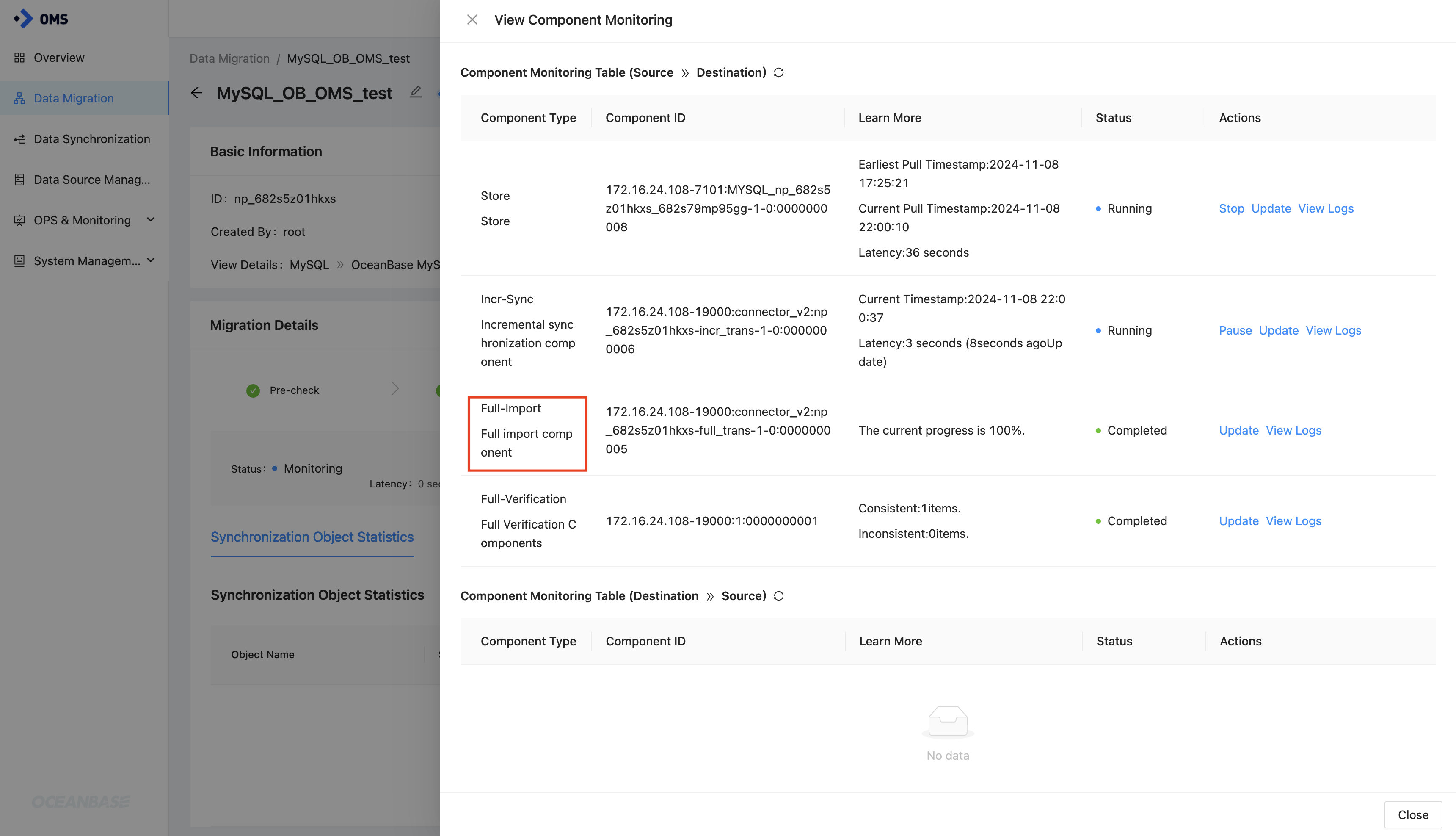
-
In the View Component Monitoring dialog box, check the component ID of the Full-Import component.
Incremental synchronization
Store
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Store |
| Log directory | /home/ds/store/store{port}/log |
| obstore (source database: OceanBase Database V3.x) | liboblog.log |
| obstore (source database: OceanBase Database V4.x) | libobcdc.log |
| mysqlstore (xlog implemented by using Java) | connector/connector.log |
Perform the following steps to query the port number of the Store component:
-
Log in to the console of OMS Community Edition.
-
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Migration.
-
On the Data Migration page, click the name of the target data migration task to go to its details page.
-
Click View Component Monitoring in the upper-right corner.

-
Click View Component Monitoring in the upper-right corner to view the component ID of the Store component.
The component ID is in the format of
{ip}-{port}:{subtopic}:{seq}, from which you can obtain the port number of the Store component.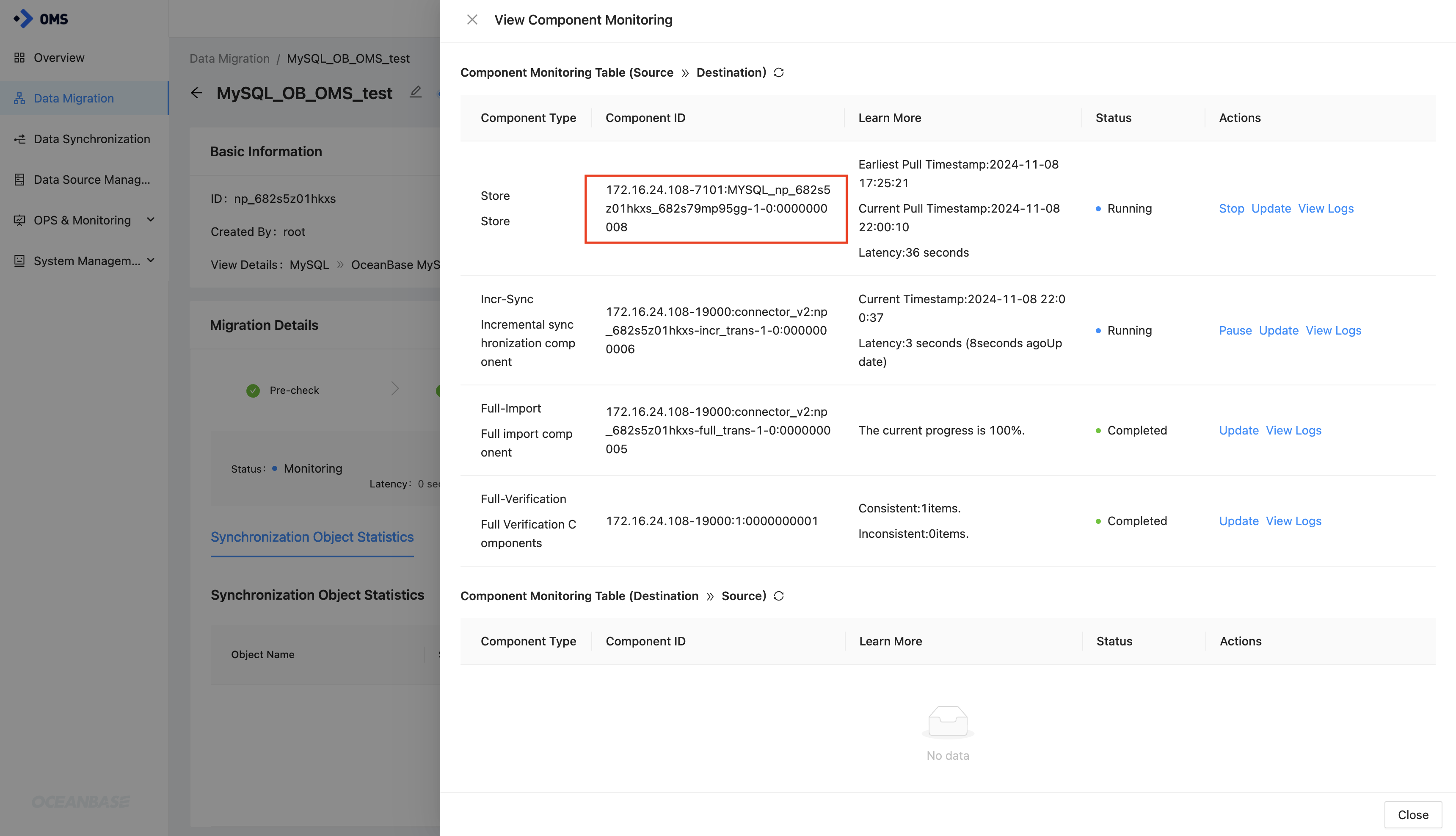
Incr-Sync
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Incr-Sync |
| Log directory | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/logs |
| Error logs | error.log |
| Operation logs | connector.log |
| Data (which contains only the primary keys) read by Incr-Sync from the source | msg/connector_source_msg.log |
| Data (which contains only the primary keys) written by Incr-Sync to the target | msg/connector_sink_msg.log |
| Data filtered by Incr-Sync | msg/connector_filter_msg.log |
Full verification
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Full-Verification |
| Log directory | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/logs |
| Error logs | error.log |
| Operation logs | task.log |
| Verification result file | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/verify/{subid}/ |
| File of inconsistent data and inconsistency reasons | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/verify/{subid}/{schema}/diff/{table_name}.diff |
| Correction SQL file that can be executed in the target | /home/ds/run/{Component ID}/verify/{subid}/{schema}/sql/{table_name}.sql |
The value of {subid} starts from 1 and increments by 1 for each reverification.
Forward switchover
Forward switchover is completed in Ghana. If you have selected Reverse Incremental Migration, a Store component and an Incr-Sync component for reverse incremental migration will be created.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Component | Ghana |
| Log directory | /home/admin/logs/ghana/Ghana |
| Common error logs | common-error.log |
| Common output logs | common-default.log |
| Task logs | oms-step.log |
| Background scheduling logs | oms-scheduler.log |
Reverse incremental migration
The content is consistent with that of the "Incremental synchronization" section, except the component ID naming format. The ID of a component for reverse incremental migration contains the reverse keyword.
Management components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| oms_console | The Ghana component, whose log directory is /home/admin/logs/ghana/Ghana. |
| oms_drc_cm | The CM component, whose log directory is /home/admin/logs/cm. |
| oms_drc_supervisor | The Supervisor component, whose log directory is /home/admin/logs/supervisor. |
Issues that May Occur During OMS Installation
Log in to the container of OMS Community Edition and check whether its components are normal. If any component is abnormal, check its logs.
supervisorctl status
The following issues often occur during installation:
-
The port is occupied.
-
You do not have required privileges on the MetaDB of OMS Community Edition.
-
The Docker environment of some operating systems has compatibility issues. The service cannot be started due to errors related to file permissions. In this case, install OMS Community Edition in another system.
-
If the user system is cgroup v2, the status of the OMS Community Edition server is abnormal. This issue is resolved in OMS of a version later than V4.2.4.
Full/Incremental Migration Performance Tuning
For more information, see Incr-Sync or Full-Import tuning.
Issues related to concurrency, Java virtual machine (JVM) memory, and number of records per slice
Most performance issues can be resolved by referring to this section.
| Issue type | Solution |
|---|---|
| Concurrency | The degree of parallelism (DOP) for the source is specified by source.workerNum, and that for the target is specified by sink.workerNum. Generally, the same DOP is specified for the source and target during full migration. You do not need to specify a DOP for the source during incremental synchronization. The DOP is subject to the number of CPU cores on the server and the maximum DOP can be four times the number of CPU cores. You also need to check whether any other migration task is running on the server. |
| JVM memory | The JVM memory is specified by coordinator.connectorJvmParam. You mainly need to adjust the -Xms8g (initial memory), -Xmx8g (maximum memory), and -Xmn4g (new memory) parameters, which must conform to the following rules:
|
| Number of records per slice | The number of records per slice is specified by the source.sliceBatchSize parameter, which defaults to 600.You can set the parameter to 10000 for a large table. If you set a larger value, much more memory will be consumed. You can determine whether to modify the source.sliceBatchSize parameter based on the slice_queue value in the metrics.log file in the logs/msg/ directory. If the value of slice_queue is 0, you need to increase the value of source.sliceBatchSize. The source worker thread pulls slices from the slice queue. The value of slice_queue being 0 indicates that no slice is available. In this case, the source worker thread will keep waiting. |
In full migration, post-indexing is usually required to improve the full migration efficiency. If the target is OceanBase Database, you can configure the DOP for index creation based on ob.parallel in the struct.transfer.config system parameter.
Incremental synchronization
The source.splitThreshold parameter specifies the transaction splitting threshold. If an incremental synchronization latency is caused by batch operations in the source, you can modify the source.splitThreshold parameter, which defaults to 128. For batch INSERT operations, you can set the parameter to a large value no greater than 512. For batch UPDATE or DELETE operations, you can set the parameter to a small value no less than 1.
Analyze logs in the metrics.log file
Identify bottlenecks
Identify bottlenecks throughout the following link: slicing > reading data from the source > distributing data > writing data to the target.
-
If the value of
slice_queueis greater than0, no bottleneck exists in slicing. The value ofslice_queuebeing0indicates that slicing is slow. In this case, you can increase the value of thesource.sliceBatchSizeparameter. In a multi-table scenario, you can also increase the value of thesource.sliceWorkerNumparameter. -
If the value of
source_worker_numis smaller than that ofsource_worker_num_all, no bottleneck exists in reading data from the source. -
If the value of
sink_worker_numis smaller than that ofsink_worker_num_all, no bottleneck exists in writing data to the target. -
If the value of
dispatcher.ready_execute_batch_sizeis0, no bottleneck exists in writing. If the value ofready_execute_batch_sizeis greater than0, writing is slow. -
If the value of
dispatcher.wait_dispatch_record_sizeis0, no bottleneck exists in data distribution. If the value ofwait_dispatch_record_sizeis greater than0, a bottleneck exists in partition calculation in OMS. Partition calculation determines to which partition data is to be distributed and is time-consuming. Therefore, data records for which partition calculation is to be performed are often accumulated for a partitioned table. In a direct load scenario, you can setsink.enablePartitionBuckettofalseto disable partition calculation. As a result, hotspot data may exist. For more information, see Suspected hotspot issues. -
If the JVM memory is insufficient, full garbage collection (GC) may occur, leading to significantly compromised overall efficiency, which may be mistakenly considered as a database disconnection error. You can log in to the container of OMS Community Edition to check the GC status.
-
If batch operations are performed in the source, we recommend that you throttle the batch operations.
su - ds
ps -ef|grep "Component ID"
/opt/alibaba/java/bin/jstat -gcutil {pid} 1s
S0 S1 E O M CCS YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT
0.00 18.27 64.08 0.90 97.11 93.45 7 0.374 0 0.000 0.374
0.00 18.27 64.08 0.90 97.11 93.45 7 0.374 0 0.000 0.374If full GC occurs frequently, you need to increase the JVM memory.
{
"jvm": {
"JVM": "{\"heapMemoryMax\":7782,\"heapMemoryInit\":8192,\"heapMemoryUsed\":1072,\"heapMemoryCommitted\":7782,\"noHeapMemoryMax\":0,\"noHeapMemoryInit\":2,\"noHeapMemoryUsed\":78,\"noHeapMemoryCommitted\":83,\"gcInfoList\":[{\"name\":\"ParNew\",\"count\":6,\"costMs\":770},{\"name\":\"ConcurrentMarkSweep\",\"count\":1,\"costMs\":362}],\"threadCount\":34}"
},
"dataflow": {
"slice_queue": 0
},
"os": {
"OS": "{\"cpu\":0.5210029306414848,\"sysCpu\":62.941847206385404}"
},
"sink": {
"sink_worker_num": 0,
"ob_watermark_detect_times": 231,
"sink_request_time": 198.43,
"source_iops": 0.0,
"sink_total_transaction": 2384.0,
"ob_exceed_mem_high_watermark_times": 0,
"sink_total_record": 23383.0,
"paused_time_ms": 0.0,
"sink_commit_time": 3363.16,
"sink_worker_num_all": 8,
"shardTime": 0.0,
"sink_total_bytes": 8739678.0,
"sink_delay": 1717642529661,
"paused_total_time_ms": 0.0,
"ob_free_memory": 92,
"rps": 41.42,
"tps": 3.1,
"ob_exceed_cpu_high_watermark_times": 0,
"iops": 3921.59,
"sinkSlowRoutes": "",
"sink_execute_time": 17.25,
"ob_free_cpu": -1
},
"source": {
"source_read_time": 0.0,
"source_rps": 0.0,
"source_slice_time": 0.0,
"source_worker_num_all": 8,
"source_worker_num": 0
},
"dispatcher": {
"wait_dispatch_record_size": 0,
"ready_execute_batch_size": 0
},
"frame": {
"SourceTaskManager.createdSourceSize": 0,
"queue_slot1.batchAccumulate": 0,
"frame.throttle.throttle_memory_remain": "2.14748365E9",
"queue_slot1.batchCount": 3715.0,
"queue_slot1.tps": 0.0
}
}
Incremental synchronization delay caused by suspected hotspots
For more information, see Suspected hotspot issues.
Full verification
-
For more information, see the "Full migration" section of this topic.
-
Specify the
task.sourceMasterSection.excludeColumnparameter to exclude columns of the large object (LOB) type and columns that do not require verification. For more information, see Parameters of the Full-Verification component.
Data Issues in Full Verification
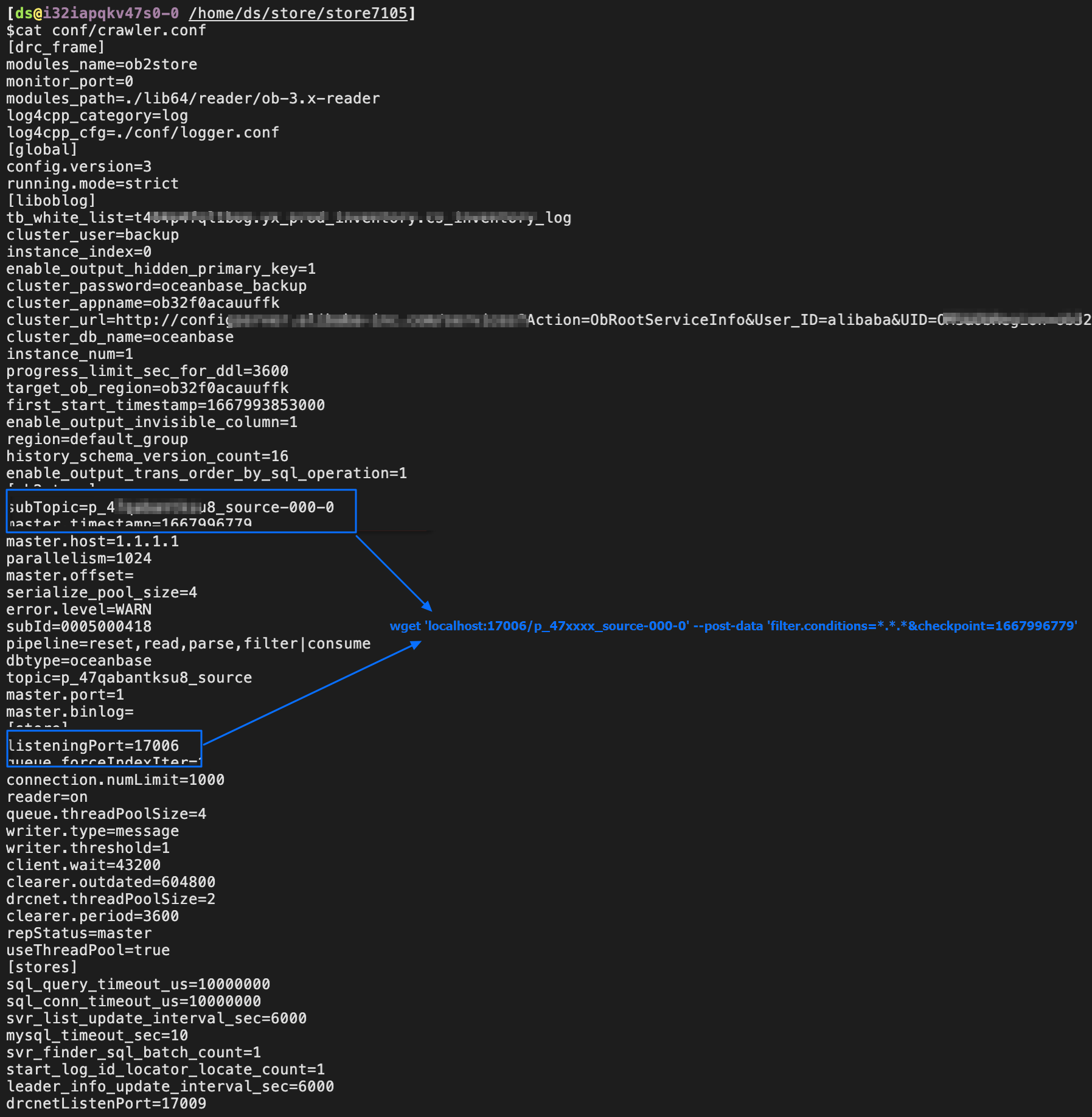
How to dump data from a Store component
# The checkpoint is a Unix timestamp.
# For the 17006 and p_47qaxxxu8_source-000-0 error codes, see the following figure.
# You can locate data by table name, time, and column content.
wget 'localhost:17006/p_47qaxxxsu8_source-000-0' --post-data 'filter.conditions=*.*.*&checkpoint=1667996779'
Typical Scenarios and Features
Multi-table aggregation
Here is an example of migrating data from multiple source tables to a single non-partitioned or partitioned table in the target.
-- Source table, primary key ID, unique key ID
CREATE TABLE test_01(id bigint not null AUTO_INCREMENT,uk_id bigint not null,...);
CREATE TABLE test_02(id bigint not null AUTO_INCREMENT,uk_id bigint not null,...);
-- Target table
CREATE TABLE test(id_new bigint not null AUTO_INCREMENT,uk_id bigint not null,...,
PRIMARY KEY (id_new,uk_id),
unique key(uk_id))
PARTITION BY HASH(uk_id)
PARTITIONS 4;
Common issues are described as follows:
-
Source tables need to be batch renamed during the creation of a data migration task. To batch rename tables, perform the following operations:
-
Select the Match Rules option.
-
Use the
src_schema.test_*=dst_schema.testsetting.
-
-
If the auto-increment ID column is used in multiple source tables, a new column name is specified as the auto-increment primary key in the target table. In this case:
-
Do not migrate the ID column in the source table to the target table, and use the
id_newcolumn as an auto-increment column in the target table. -
Set
sink.ignoreRedunantColumnsReplicatetotrueto ignore the ID column during full migration. -
Set
sink.ignoreRedunantColumnsReplicatetotrueto ignore the ID column during incremental synchronization.
-
-
In OceanBase Database, the primary key must contain the partitioning key if the target is a partitioned table. To enable support for data verification, perform the following operations:
-
Set
task.sourceMasterSection.matchAllColumntofalseto skip the ID column during full verification. The source table must have a non-null unique key. Otherwise, verification is not supported. -
Use the
filter.verify.inmod.tables=.*;.*;.*setting to enable the IN mode for full verification. For more information, see Parameters of the Full-Verification component.
-
Migration of a table without a primary key from OceanBase Database, with a hidden column added in the target
When migrating a table without a primary key from OceanBase Database Community Edition, OMS Community Edition will use a hidden column __pk_increment as the primary key. During schema migration, an OMS_PK_INCRMT column will be added to the target table.
-
The
OMS_PK_INCRMTcolumn will be deleted after a forward switchover. -
If no forward switchover is performed and the target database serves as the source database in the next task, an exception will occur. In this case, you must manually delete the
OMS_PK_INCRMTcolumn.
Direct load
Apart from concurrency parameters, the direct load performance is also subject to the sink.serverParallel parameter, which defaults to 8. This parameter will affect the number of worker threads and concurrency for direct load tasks on the OBServer node.
Reverse incremental migration
If you want to roll back the database or use the source database as a standby database, we recommend that you select Reverse Incremental Migration when you create a data migration task. When you migrate data from a MySQL database to OceanBase Database Community Edition, you need to manually create a transaction database named omstxndb in the MySQL database, which will be used by OMS Community Edition. If you do not create this transaction database, an error prompting that the omstxndb database does not exist will be returned.
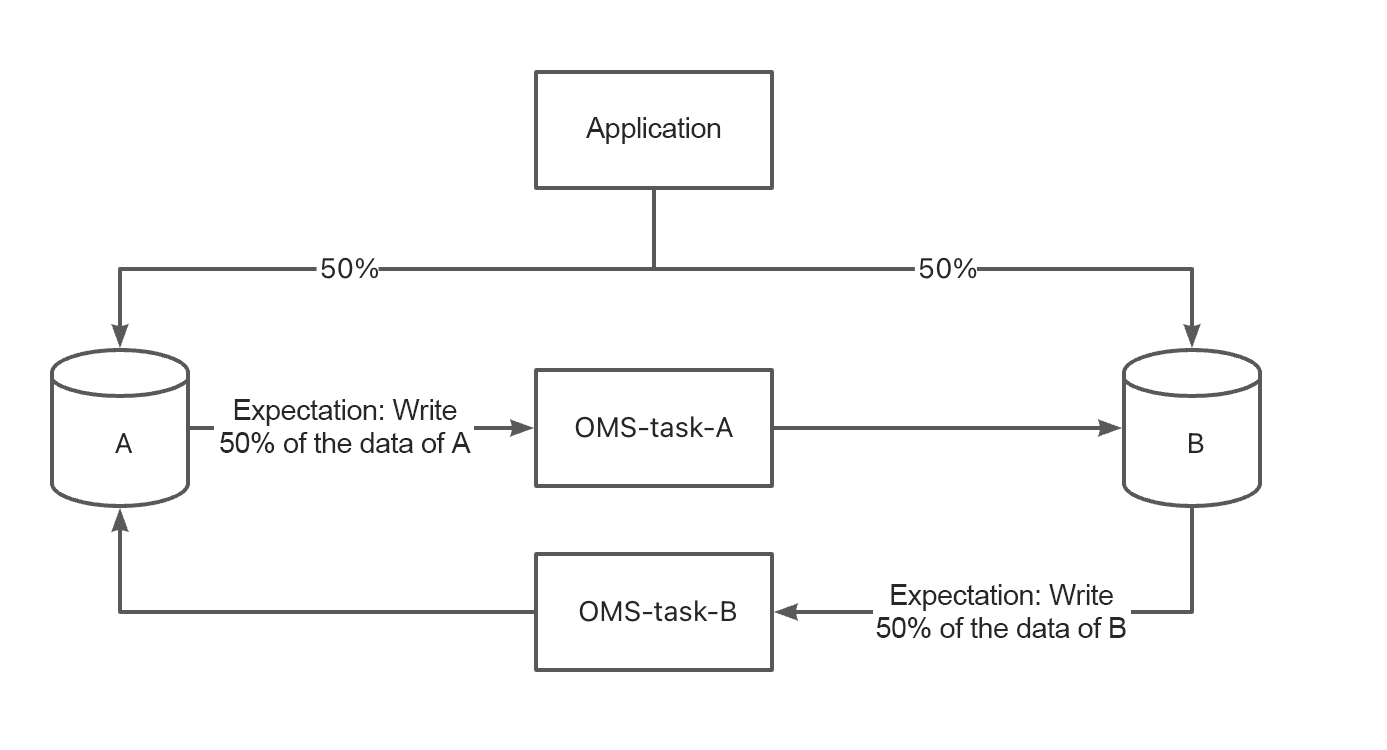
Active-active disaster recovery
If double write or canary switching is required, you can use the active-active disaster recovery feature of OMS Community Edition. At present, this feature is supported when you migrate data from a MySQL database to OceanBase Database Community Edition, or migrate data within OceanBase Database Community Edition. OMS Community Edition automatically sets cyclical replication prevention parameters. In an active-active disaster recovery scenario, all tables must have a primary key or unique key.
-
Two databases named A and B exist.
-
An application writes data to A and B based on certain rules.
Non-double write means that data written to one database will not be written to the other database.
-
Both A and B store all data of the application.
Full verification
Two full verification modes are supported:
-
Default mode: Data is queried based on the slice scope in both the source and target databases.
-
IN mode: Data is queried based on the slice scope in the source database. Data is queried in the target database by using the primary key or unique key in the data queried from the source database. You can enable the IN mode by using the
filter.verify.inmod.tablesparameter.Here are some examples:
-
Enable IN mode verification for all tables of the current task:
filter.verify.inmod.tables=.*;.*;.* -
Enable IN mode verification for the
T1table in theD1database:filter.verify.inmod.tables=D1;T1;.* -
Enable IN mode verification for the
T1andT2tables in theD1database:filter.verify.inmod.tables=D1;T1;.*|D1;T2;.* -
Enable IN mode verification for the
T1andT2tables in theD1database and theT3andT4tables in theD2database:filter.verify.inmod.tables=D1;T1;.*|D1;T2;.*|D2;T3;.*|D2;T4;.*
-
System Views Used in OMS Community Edition
MySQL
System tables and views
| Table/View | Description |
|---|---|
| information_schema.SCHEMATA | Stores information about schemas. |
| information_schema.tables | Stores information about tables. |
| information_schema.columns | Stores information about columns. |
| information_schema.STATISTICS | Stores information about table indexes. |
SQL statements
SET TIME_ZONE='%s';
SET sql_mode='';
SET names 'utf8mb4';
SET foreign_key_checks = off;
SELECT version();
SELECT 1;
-- Query information about all schemas.
SELECT CATALOG_NAME, SCHEMA_NAME, DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET_NAME, DEFAULT_COLLATION_NAME, SQL_PATH
FROM `information_schema`.`SCHEMATA`
-- Query information about all tables.
SELECT NULL,TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_ROWS, TABLE_COLLATION, ENGINE
FROM information_schema.tables WHERE TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE' AND TABLE_SCHEMA NOT IN('mysql','information_schema','performance_schema')
-- Query the database engine of a table.
SELECT `ENGINE` FROM `information_schema`.`tables` WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '%s' AND TABLE_NAME = '%s'
-- Query the character set of a table.
SELECT TABLE_COLLATION FROM information_schema.tables WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '%s' AND TABLE_NAME = '%s'
-- Query information about columns.
SELECT `COLUMN_NAME` ,upper(`COLUMN_TYPE`) ,`CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH` ,`NUMERIC_PRECISION`,`NUMERIC_SCALE`
FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION ASC
-- Query all views.
SELECT TABLE_NAME, TABLE_SCHEMA, VIEW_DEFINITION FROM information_schema.views
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA IN ('xx');
-- Query only regular columns, excluding generated columns.
SELECT `COLUMN_NAME` ,upper(`COLUMN_TYPE`) ,`CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH` ,`NUMERIC_PRECISION`,`NUMERIC_SCALE`
FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? AND (GENERATION_EXPRESSION='' or GENERATION_EXPRESSION is null) ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION ASC
-- Query indexes.
SELECT INDEX_NAME,NON_UNIQUE,SEQ_IN_INDEX,COLUMN_NAME,SUB_PART FROM information_schema.STATISTICS WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=?
AND concat(index_schema,'.',index_name) NOT IN (
SELECT concat(index_schema,'.',index_name) FROM information_schema.STATISTICS
WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? AND upper(nullable)='YES')
ORDER BY INDEX_NAME ASC, SEQ_IN_INDEX ASC
-- Query partitions.
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME,PARTITION_NAME,SUBPARTITION_NAME,PARTITION_METHOD,PARTITION_EXPRESSION,SUBPARTITION_METHOD,SUBPARTITION_EXPRESSION
FROM information_schema.PARTITIONS
-- Query constraints.
SELECT REFERENCED_TABLE_SCHEMA, REFERENCED_TABLE_NAME, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, CONSTRAINT_NAME,REFERENCED_COLUMN_NAME, COLUMN_NAME FROM information_schema.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE
MySQL tenant of OceanBase Database
System tables and views
| Table/View | Description |
|---|---|
| information_schema.SCHEMATA | Stores information about schemas. |
| information_schema.tables | Stores information about tables. |
| information_schema.columns | Stores information about columns. |
| information_schema.STATISTICS | Stores information about table indexes. |
| information_schema.PARTITIONS | Stores information about partitions. |
| oceanbase.gv$memstore | Stores memory usage information. |
| oceanbase.gv$sysstat | Stores CPU utilization information. |
| oceanbase.gv$table | Stores table IDs. |
| oceanbase.__tenant_virtual_table_index | Stores information about indexes. |
| The following system tables are required for dividing data into macroblocks. | |
| oceanbase.__all_tenant | Stores information about tenants. |
| oceanbase.__all_database | Stores information about databases. |
| oceanbase.__all_table | Stores information about tables. |
| oceanbase.__all_part | Stores information about partitions. |
| oceanbase.__all_meta_table | Stores table metadata. |
| oceanbase.__all_virtual_database | Stores information about databases. |
| oceanbase.__all_virtual_table | Stores information about tables. |
| oceanbase.__all_virtual_proxy_partition | Stores information about partitions. |
| oceanbase.__all_meta_table | Stores metadata. |
| oceanbase.__all_virtual_partition_item | Stores information about subpartitions. |
| oceanbase.__all_virtual_partition_sstable_macro_info | Stores information about macroblocks. |
Note
Macroblock information can be queried only from the sys tenant.
SQL statements
-- Query information about all schemas.
SELECT CATALOG_NAME, SCHEMA_NAME, DEFAULT_CHARACTER_SET_NAME, DEFAULT_COLLATION_NAME, SQL_PATH
FROM `information_schema`.`SCHEMATA`
-- Query information about all tables.
SELECT NULL,TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_ROWS, TABLE_COLLATION, ENGINE
FROM information_schema.tables WHERE TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE' AND TABLE_SCHEMA NOT IN('mysql','information_schema','performance_schema')
-- Query the database engine of a table.
SELECT `ENGINE` FROM `information_schema`.`tables` WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '%s' AND TABLE_NAME = '%s'
-- Query the character set of a table.
SELECT TABLE_COLLATION FROM information_schema.tables WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = '%s' AND TABLE_NAME = '%s'
-- Query column information.
SELECT `COLUMN_NAME` ,upper(`COLUMN_TYPE`) ,`CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH` ,`NUMERIC_PRECISION`,`NUMERIC_SCALE`
FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION ASC
-- Query only regular columns, excluding generated columns.
SELECT `COLUMN_NAME` ,upper(`COLUMN_TYPE`) ,`CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH` ,`NUMERIC_PRECISION`,`NUMERIC_SCALE`
FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? AND (GENERATION_EXPRESSION='' or GENERATION_EXPRESSION is null) ORDER BY ORDINAL_POSITION ASC
-- Query indexes.
SELECT INDEX_NAME,NON_UNIQUE,SEQ_IN_INDEX,COLUMN_NAME,SUB_PART FROM information_schema.STATISTICS WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=?
AND concat(index_schema,'.',index_name) NOT IN (
SELECT concat(index_schema,'.',index_name) FROM information_schema.STATISTICS
WHERE table_schema=? AND table_name=? AND upper(nullable)='YES')
ORDER BY INDEX_NAME ASC, SEQ_IN_INDEX ASC
-- Query partition information.
SELECT PARTITION_NAME,SUBPARTITION_NAME FROM information_schema.PARTITIONS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='{}' AND TABLE_NAME='{}'
-- Query the partitioning key expression.
SELECT DISTINCT PARTITION_EXPRESSION,SUBPARTITION_EXPRESSION FROM information_schema.PARTITIONS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA=? AND TABLE_NAME=?
-- Query tenant information.
SELECT tenant_id FROM oceanbase.__all_tenant WHERE tenant_name = '%s'
-- Query indexes in a table.
SELECT key_name, NON_UNIQUE,SEQ_IN_INDEX,COLUMN_NAME,`null` nullable FROM oceanbase.__tenant_virtual_table_index WHERE table_id = ?
-- Query the ID of a table.
-- Versions earlier than 20200
SELECT %s b.table_id FROM oceanbase.__all_database a, oceanbase.__all_table b WHERE a.database_id = b.database_id AND a.tenant_id = %d AND a.database_name = '%s' AND b.table_name = '%s'
-- Versions later than 20200
SELECT %s b.table_id FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_database a, oceanbase.__all_virtual_table b WHERE a.database_id = b.database_id AND a.tenant_id = %d AND a.database_name = '%s' AND b.table_name = '%s'
-- Query partition information.
-- Versions earlier than 20200
SELECT %s part_id,part_name FROM oceanbase.__all_part WHERE table_id = %d AND part_name IS NOT NULL AND part_name<>''
-- Versions later than 20200
SELECT %s part_id,part_name FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_proxy_partition WHERE table_id = %d AND part_name IS NOT NULL AND part_name<>''
-- Query subpartition information.
SELECT %s partition_id,case when subpart_name is null then concat(part_name,'sp',subpart_id) ELSE subpart_name END subpart_name FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_partition_item WHERE table_id = %d AND partition_level>1
-- Query the ID of a table.
SELECT table_id FROM oceanbase.gv$table WHERE database_name=? AND table_name=?
-- Query macroblock information. store_type=1 indicates normal information, and store_type=4 indicates minor compaction information.
-- Versions earlier than 20200
SELECT %s partition_id OMS_PARTITION_ID,data_seq OMS_DATA_SEQ,macro_range OMS_MACRO_RANGE,row_count OMS_ROW_COUNT FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_partition_sstable_macro_info
WHERE tenant_id=%d AND table_id = %d AND store_type=1 AND macro_range NOT LIKE '%%]always true' AND macro_range<>'(MIN ; MAX]' AND macro_range LIKE '%%]'
AND (svr_ip,svr_port,partition_id) IN (SELECT svr_ip, svr_port,partition_id FROM oceanbase.__all_meta_table
WHERE tenant_id=%d AND table_id = %d AND ROLE = 1)
ORDER BY partition_id,data_seq
-- Versions later than 20200
SELECT %s partition_id OMS_PARTITION_ID,data_seq OMS_DATA_SEQ,macro_range OMS_MACRO_RANGE,row_count OMS_ROW_COUNT FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_partition_sstable_macro_info
WHERE tenant_id=%d AND table_id = %d AND store_type=1 AND macro_range NOT LIKE '%%]always true' AND macro_range<>'(MIN ; MAX]' AND macro_range LIKE '%%]'
AND (svr_ip,svr_port,partition_id) IN (SELECT svr_ip, svr_port,partition_id FROM oceanbase.__all_virtual_meta_table
WHERE tenant_id=%d AND table_id = %d AND ROLE = 1)
ORDER BY partition_id,data_seq
-- Memory resource exhaustion prevention
SELECT /*+query_timeout(5000000)*/ total, freeze_trigger,mem_limit FROM oceanbase.gv$memstore
-- CPU resource exhaustion prevention
SELECT min(100-round(cpu_usage.value * 100 / cpu_limit.value)) cpu_free_percent
FROM oceanbase.gv$sysstat cpu_usage, oceanbase.gv$sysstat cpu_limit
WHERE cpu_usage.name = 'cpu usage' AND cpu_limit.name = 'max cpus'
AND cpu_usage.svr_ip = cpu_limit.svr_ip
Others
Hot update for the CDC library
OceanBase Database of each version provides a corresponding Change Data Capture (CDC) library for pulling incremental logs. The Store component of OMS Community Edition loads the CDC dynamic library to pull incremental data from OceanBase Database.
The following table lists the subdirectories in the /home/ds/lib64/reader directory of the Store component that are corresponding to OceanBase CDC libraries of different versions.
| Store component | OceanBase CDC library |
|---|---|
| ob-ce-reader | Hot updates not supported |
| ob-ce-4.x-reader | OceanBase Database of a version from V4.0.0 to V4.2.1 |
| ob-ce-4.2.2-reader | OceanBase Database of a version from V4.2.2 to V4.3.0 |
| ob-ce-4.3-reader | OceanBase Database V4.3.0 and later |
The hot update procedure is as follows:
-
Download the RPM package of OceanBase CDC from OceanBase Download Center.
-
Run the following command to decompress the RPM package:
rpm2cpio oceanbase-ce-cdc-x.x.x.x-xxxx.el7.x86_64.rpm|cpio -idmu --quiet. -
After the decompression, the following files appear in the
./home/admin/oceanbase/lib64directory:libobcdc.so.x.x.x.x
libobcdc.so.x -> libobcdc.so.x.x.x.x
libobcdc.so -> libobcdc.so.x -
Log in to the container of OMS Community Edition and run the
cdcommand to go to the/home/ds/lib64/readerdirectory. Find the correspondingob-ce-xxx-readerdirectory based on the version of OceanBase Database. -
Back up the original files in the
ob-ce-xxx-readerdirectory. -
Copy the files in the
./home/admin/oceanbase/lib64directory extracted from the RPM package to theob-ce-xxx-readerdirectory.
Then, all new Store components will use the updated CDC library. To perform a hot update for an existing Store component, perform the following steps:
-
Go to the runtime directory
/home/ds/store/store{port}/lib64/readerof the Store component. The directory structure is consistent with that of/home/ds/lib64/reader. -
Copy the files in the
./home/admin/oceanbase/lib64directory extracted from the RPM package to the/home/ds/store/store{port}/lib64/reader/ob-ce-xxx-readerdirectory. -
Log in to the console of OMS Community Edition and pause the Store component. For more information, see Start and pause a store.
-
Run the following command to check whether the Store process has been stopped. If not, run the
kill -9command.ps -ef | grep store{port} -
In the console of OMS Community Edition, start the Store component.