2.5 View the resource usage of an OceanBase cluster
Before business development, the DBA must create a database instance (tenant) in the OceanBase cluster. An OceanBase cluster supports multiple tenants. This architecture is called multitenancy.
Working mechanism of multitenancy
OceanBase Database is deployed and run as a cluster and provides tenants in the cluster for business systems. In a sense, tenants are comparable to "instances" in a conventional database system. In OceanBase Database, tenants are totally isolated. In terms of data security, OceanBase Database forbids cross-tenant access to prevent data assets of a tenant from being stolen by other tenants. In terms of resource usage, OceanBase Database ensures that tenants "exclusively" occupy their allocated resource quotas. In summary, a tenant can be seen as a container for database objects and resources such as CPU, memory, and I/O resources.
OceanBase Database is a single-process software solution. Its process is named observer. By default, the observer process will occupy most of the CPU, memory, and disk resources in the operating system after it is started. You can use cluster startup parameters to specify the amount of resources that you want to allocate to the process.
As shown in the following figure, an OceanBase cluster can manage all resources allocated to the observer process in a centralized manner and allocate the resources to tenants. You can define the resource specifications for a tenant and adjust the resource specifications online.
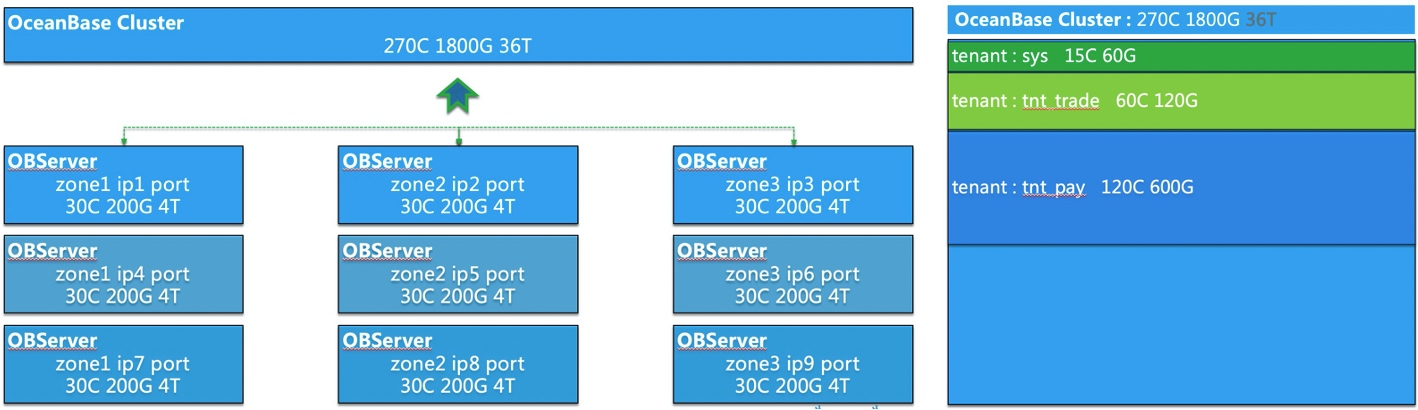
The resources for an OceanBase Database tenant include CPU, memory, and IOPS. At present, OceanBase Database supports the isolation of these resources. We recommend that you set the resource parameters based on the actual situation when you create resources. For example, the value of the parameter related to the disk space should not exceed the actual available disk space. Otherwise, load balancing is affected.
Note
Among the resources allocated to the
observerprocess, the number of CPU cores is declaratory, and the memory and disk resources are exclusive (preallocated).
View available resources of a cluster
To ensure sufficient resources when you create user tenants, you must calculate the remaining available resources of the cluster. Each OceanBase cluster has a default tenant named sys. You can view and manage the resources in a cluster from the sys tenant. You can log on to the sys tenant of a cluster as the root user and execute the following statement to view the available resources of the cluster.
View available resources of the cluster
SELECT ZONE,SVR_IP,SVR_PORT,
CPU_CAPACITY,
CPU_ASSIGNED,
CPU_CAPACITY-CPU_ASSIGNED AS CPU_MIN_FREE,
CPU_CAPACITY_MAX,
CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX,
CPU_CAPACITY_MAX-CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX AS CPU_MAX_FREE,
ROUND(MEMORY_LIMIT/1024/1024/1024,2) AS MEMORY_TOTAL_GB,
ROUND((MEMORY_LIMIT-MEM_CAPACITY)/1024/1024/1024,2) AS SYSTEM_MEMORY_GB,
ROUND(MEM_ASSIGNED/1024/1024/1024,2) AS MEM_ASSIGNED_GB,
ROUND((MEM_CAPACITY-MEM_ASSIGNED)/1024/1024/1024,2) AS MEMORY_FREE_GB,
ROUND(LOG_DISK_CAPACITY/1024/1024/1024,2) AS LOG_DISK_CAPACITY_GB,
ROUND(LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED/1024/1024/1024,2) AS LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED_GB,
ROUND((LOG_DISK_CAPACITY-LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED)/1024/1024/1024,2) AS LOG_DISK_FREE_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_CAPACITY/1024/1024/1024),2) AS DATA_DISK_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_IN_USE/1024/1024/1024),2) AS DATA_DISK_USED_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_CAPACITY-DATA_DISK_IN_USE)/1024/1024/1024,2) AS DATA_DISK_FREE_GB
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_SERVERS;
The output is as follows:
+-------+----------------+----------+--------------+--------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+--------------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| ZONE | SVR_IP | SVR_PORT | CPU_CAPACITY | CPU_ASSIGNED | CPU_MIN_FREE | CPU_CAPACITY_MAX | CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX | CPU_MAX_FREE | MEMORY_TOTAL_GB | SYSTEM_MEMORY_GB | MEM_ASSIGNED_GB | MEMORY_FREE_GB | LOG_DISK_CAPACITY_GB | LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED_GB | LOG_DISK_FREE_GB | DATA_DISK_GB | DATA_DISK_USED_GB | DATA_DISK_FREE_GB |
+-------+----------------+----------+--------------+--------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+--------------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| zone1 | 10.10.10.1 | 2882 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 11 | 20.00 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 48.00 | 15.00 | 33.00 | 30.00 | 6.82 | 23.18 |
| zone2 | 10.10.10.2 | 2882 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 11 | 20.00 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 48.00 | 15.00 | 33.00 | 30.00 | 8.91 | 21.09 |
| zone3 | 10.10.10.3 | 2882 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 11 | 20.00 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 48.00 | 15.00 | 33.00 | 30.00 | 8.91 | 21.09 |
+-------+----------------+----------+--------------+--------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+--------------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
The following table describes the fields.
| Field | Type | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZONE | varchar(128) | NO | The name of the zone. |
| SVR_IP | varchar(46) | NO | The IP address of the server. |
| SVR_PORT | bigint(20) | NO | The port number of the server. |
| CPU_CAPACITY | bigint(20) | NO | The total CPU capacity of the OBServer node. |
| CPU_CAPACITY_MAX | double | NO | The overprovisioning value for the total CPU capacity of the OBServer node. It is subject to the resource_hard_limit parameter. The following rule applies: CPU_CAPACITY_MAX = CPU_CAPACITY × resource_hard_limit |
| CPU_ASSIGNED | double | NO | The number of allocated CPU cores for the OBServer node. It is the sum of the MIN_CPU values of all units on the OBServer node. The following rule applies: CPU_ASSIGNED <= CPU_CAPACITY |
| CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX | double | NO | The maximum number of allocated CPU cores for the OBServer node. It is the sum of the MAX_CPU values of all units on the OBServer node. The following rule applies: CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX <= CPU_CAPACITY_MAX |
| MEM_CAPACITY | bigint(20) | NO | The size of memory available for the observer process. |
| MEM_ASSIGNED | bigint(20) | NO | The size of allocated memory for the OBServer node. It is the sum of the MEMORY_SIZE values of all units on the OBServer node. The following rule applies: MEM_ASSIGNED <= MEM_CAPACITY |
| LOG_DISK_CAPACITY | bigint(20) | NO | The total size of the log disk. |
| LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED | bigint(20) | NO | The size of allocated space of the log disk. It is the sum of the MAX_DISK_SIZE values of all units on the OBServer node. |
| LOG_DISK_IN_USE | bigint(20) | NO | The size of used space of the log disk. |
| DATA_DISK_CAPACITY | bigint(20) | NO | The total size of the data disk. |
| DATA_DISK_IN_USE | bigint(20) | NO | The size of used space of the data disk. |
View the unit config
SELECT * FROM oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS;
The output is as follows:
+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
| UNIT_CONFIG_ID | NAME | CREATE_TIME | MODIFY_TIME | MAX_CPU | MIN_CPU | MEMORY_SIZE | LOG_DISK_SIZE | MAX_IOPS | MIN_IOPS | IOPS_WEIGHT |
+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
| 1 | sys_unit_config | 2024-02-19 15:33:47.524052 | 2024-02-19 15:33:47.524052 | 2 | 2 | 1073741824 | 3221225472 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 2 |
+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
The following table describes the fields.
| Field | Type | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNIT_CONFIG_ID | bigint(20) | NO | The ID of the unit config. |
| NAME | varchar(128) | NO | The name of the unit config. |
| CREATE_TIME | timestamp(6) | YES | The time when the unit config was created. |
| MODIFY_TIME | timestamp(6) | YES | The time when the unit config was last modified. |
| MAX_CPU | double | NO | The maximum number of CPU cores. |
| MIN_CPU | double | NO | The minimum number of CPU cores. |
| MEMORY_SIZE | bigint(20) | NO | The memory size, in bytes. |
| LOG_DISK_SIZE | bigint(20) | NO | The log disk size, in bytes. |
| MAX_IOPS | bigint(20) | NO | The maximum disk IOPS. |
| MIN_IOPS | bigint(20) | NO | The minimum disk IOPS. |
| IOPS_WEIGHT | bigint(20) | NO | The IOPS weight. |
View the resource allocation details
SELECT T4.TENANT_ID,T4.TENANT_NAME,
T1.NAME RESOURCE_POOL_NAME, T1.UNIT_COUNT,
T2.`NAME` UNIT_CONFIG_NAME,
T2.MAX_CPU, T2.MIN_CPU,
ROUND(T2.MEMORY_SIZE/1024/1024/1024,2) MEM_SIZE_GB,
ROUND(T2.LOG_DISK_SIZE/1024/1024/1024,2) LOG_DISK_SIZE_GB, T2.MAX_IOPS,
T2.MIN_IOPS, T3.UNIT_ID, T3.ZONE, CONCAT(T3.SVR_IP,':' ,T3.`SVR_PORT`) OBSERVER
FROM oceanbase.DBA_OB_RESOURCE_POOLS T1
JOIN oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS T2 ON (T1.UNIT_CONFIG_ID=T2.UNIT_CONFIG_ID)
JOIN oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNITS T3 ON (T1.`RESOURCE_POOL_ID` = T3.`RESOURCE_POOL_ID`)
LEFT JOIN oceanbase.DBA_OB_TENANTS T4 ON (T1.TENANT_ID=T4.TENANT_ID)
ORDER BY T4.TENANT_NAME,T3.ZONE;
The output is as follows. For more information about the views referenced in the statement, see Outline of system views.
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+--------------------+
| TENANT_ID | TENANT_NAME | RESOURCE_POOL_NAME | UNIT_COUNT | UNIT_CONFIG_NAME | MAX_CPU | MIN_CPU | MEM_SIZE_GB | LOG_DISK_SIZE_GB | MAX_IOPS | MIN_IOPS | UNIT_ID | ZONE | OBSERVER |
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+--------------------+
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 1 | zone1 | 10.10.10.1 :2882 |
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 2 | zone2 | 10.10.10.1 :2882 |
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 3 | zone3 | 10.10.10.1 :2882 |
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+--------------------+
As shown in the output, the resource pool of the sys tenant consists of the resource units on nodes in all the zones. The resource units share the same unit config (sys_unit_config).