2.6 Create a MySQL user tenant
We recommend that you create a user tenant by referring to this topic for testing or business purposes. It is prohibited to use the sys tenant for such purposes.
Notice
OceanBase Database Community Edition supports creating only MySQL tenants.
Create a tenant by using OCP
Note
This section briefly describes how to create a tenant by using OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP). For more information, see Create a tenant.
-
Configure tenant information as shown in the following figure.
If no unit config is suitable, you can create one. After you create a unit config in OCP, it is not immediately recorded in the internal view
DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGSof OceanBase Database, but rather in themeta_database.ob_unit_spectable of OCP. The unit config is actually created only when you create a tenant.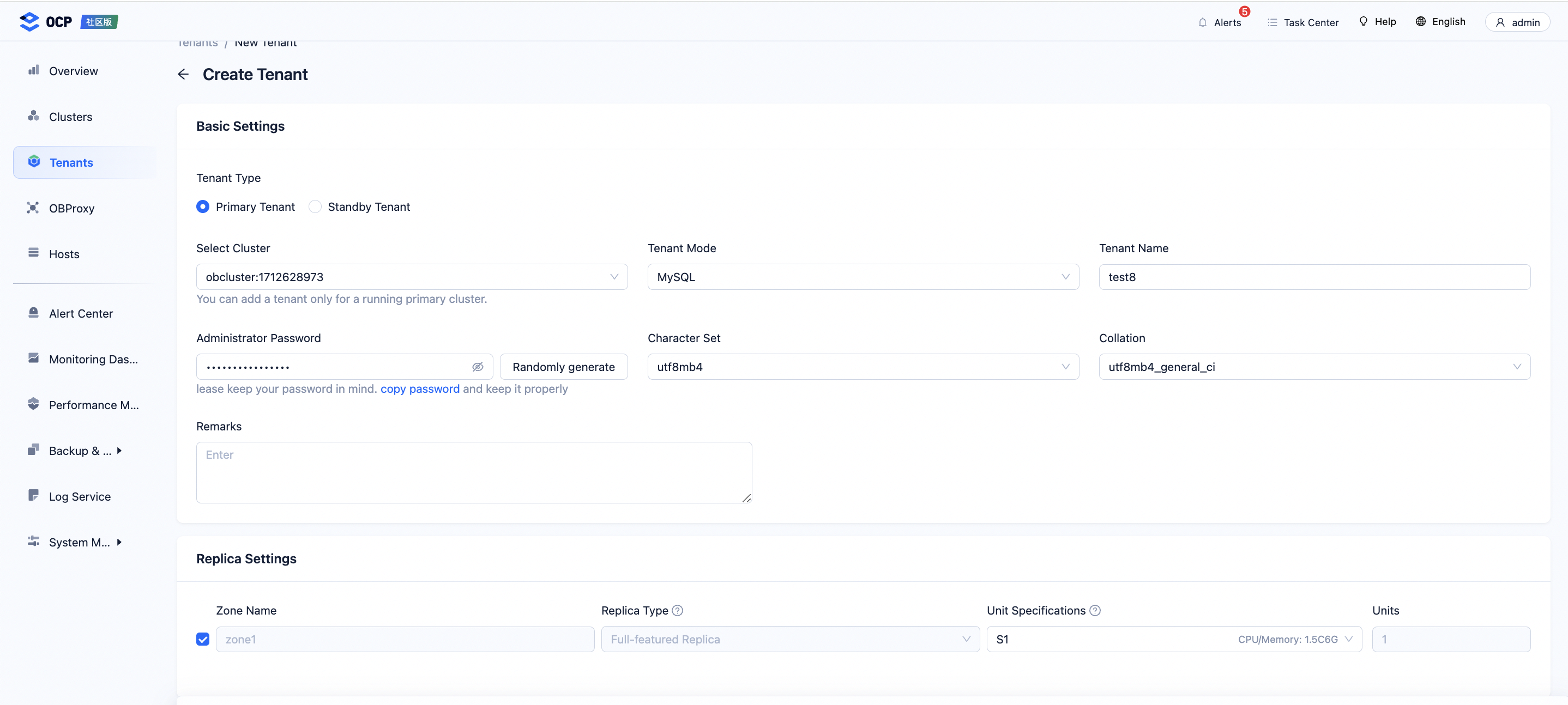
-
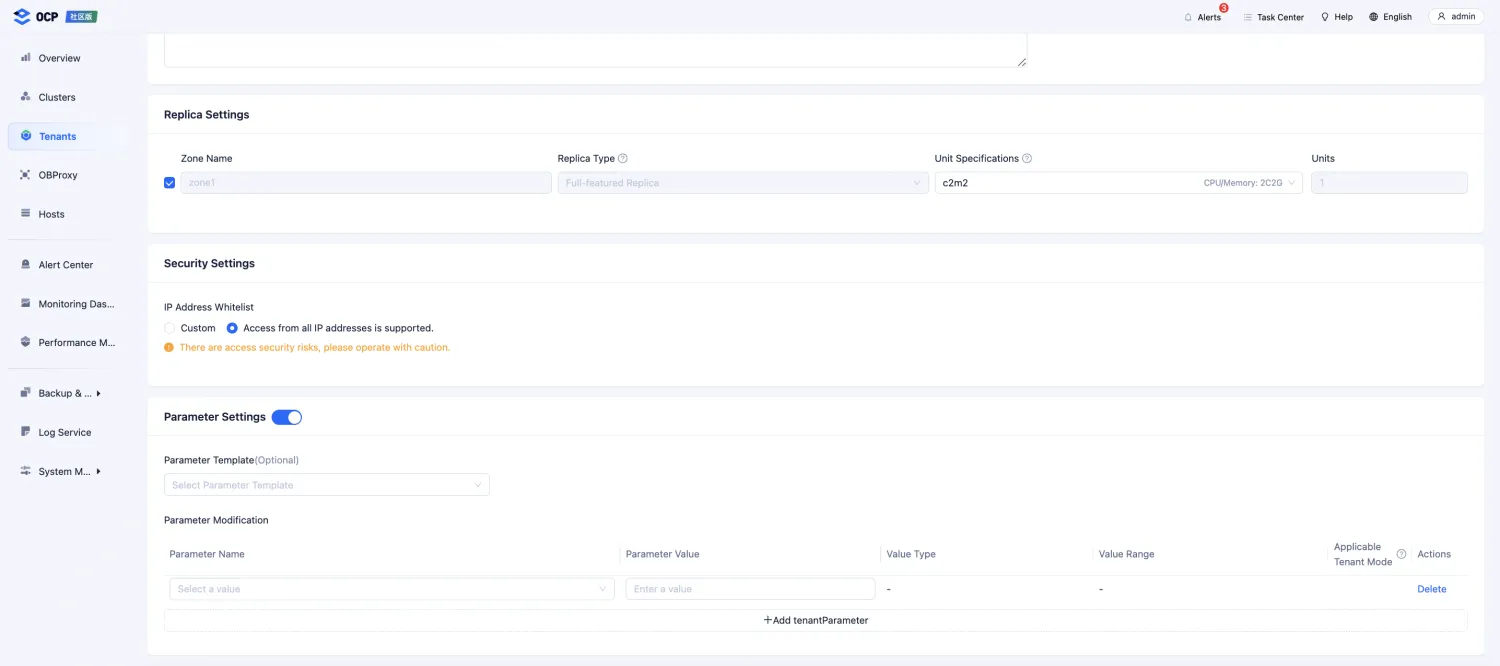
Configure the IP address allowlist and variables of the tenant.
-
View the tenant creation task.
To learn about the task execution process, you can download the logs.
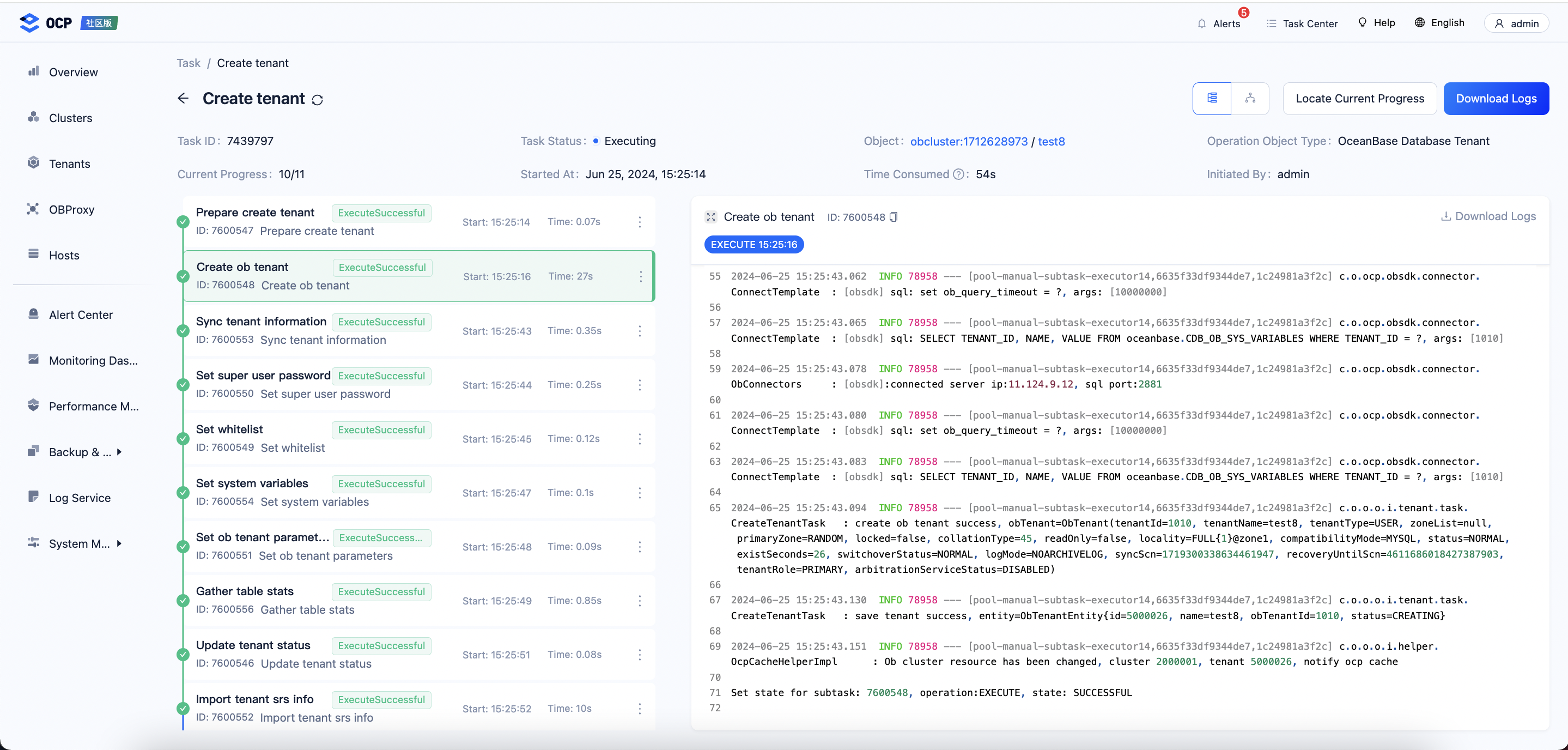
You can learn from the logs that OCP will respectively name each unit and resource pool during tenant creation, which is not the case when you create a tenant in OceanBase Deployer (OBD). This practice brings the following benefits:
-
Units are not reused. Adjusting the unit config of one tenant will not affect other tenants.
-
Resource pools are not reused. After an OBServer node is deleted, you do not need to split resource pools for tenants on the node.
-
Create a tenant by using an OBD command
If the cluster where a tenant is to be created is managed by OBD, you can use an OBD command to create the tenant. If the cluster where a tenant is to be created is not managed by OBD, the cluster version is OceanBase Database Community Edition V4.2.1 BP4 or later, and OBShell has been started, you can first run a takeover command and then run the following OBD command to create the tenant. For more information about the takeover, see OceanBase Deployer Documentation Center.
obd cluster tenant create obtest -n test2 \
--max-cpu=2 --memory-size=2G --log-disk-size=3G --max-iops=10000 \
--unit-num=1 --charset=utf8 -s 'ob_tcp_invited_nodes="%"'
For more information about the obd cluster tenant create command, see the obd cluster tenant create section in Cluster commands.
-
In this command,
obtestis a sample cluster name (deploy name). You can run theobd cluster listcommand and replaceobtestwith a value in theNamecolumn of the output. -
test2is a sample tenant name. -
The resource unit and resource pool used by a tenant created by using the OBD command are respectively named
${tenant_name}_unitand${tenant_name}_pool. -
Note: When creating a tenant using OBD, the maximum occupancy mode is used by default. If resources are tight or you want to create a tenant in the minimum availability mode, it is recommended to use OCP or SQL first.
The output is as follows:
Get local repositories and plugins ok
Open ssh connection ok
Connect to observer 10.10.10.1:2881 ok
Create tenant test2 ok
Trace ID: 4af55084-cf17-11ee-b825-00163e04608d
If you want to view detailed obd logs, please run: obd display-trace 4af55084-cf17-11ee-b825-00163e04608d
You can copy and run the obd display command in the output to view the logs that record the detailed creation process.
obd display-trace 4af55084-cf17-11ee-b825-00163e04608d
The output is as follows:
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.385] [DEBUG] - cmd: ['obtest']
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.385] [DEBUG] - opts: {'tenant_name': 'test2', 'max_cpu': 2.0, 'min_cpu': None, 'max_memory': None, 'min_memory': None, 'memory_size': '2G', 'max_disk_size': None, 'log_disk_size': '3G', 'max_iops': 10000, 'min_iops': None, 'iops_weight': None, 'max_session_num': None, 'unit_num': 1, 'zone_list': None, 'mode': 'mysql', 'charset': 'utf8', 'collate': None, 'replica_num': None, 'logonly_replica_num': None, 'tablegroup': None, 'primary_zone': 'RANDOM', 'locality': None, 'variables': 'ob_tcp_invited_nodes="%"'}
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.385] [DEBUG] - mkdir /home/admin/.obd/lock/
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.385] [DEBUG] - unknown lock mode
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - try to get share lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/global
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - share lock `/home/admin/.obd/lock/global`, count 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - Get Deploy by name
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - mkdir /home/admin/.obd/cluster/
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - mkdir /home/admin/.obd/config_parser/
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - try to get exclusive lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/deploy_obtest
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.386] [DEBUG] - exclusive lock `/home/admin/.obd/lock/deploy_obtest`, count 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.390] [DEBUG] - Deploy status judge
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.390] [DEBUG] - Get deploy config
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.407] [INFO] Get local repositories and plugins
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.407] [DEBUG] - mkdir /home/admin/.obd/repository
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.407] [DEBUG] - Get local repository oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.407] [DEBUG] - try to get share lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.408] [DEBUG] - share lock `/home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo`, count 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.409] [DEBUG] - Get local repository obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0-0aed4b782120e4248b749f67be3d2cc82cdcb70d
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.409] [DEBUG] - share lock `/home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo`, count 2
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.410] [DEBUG] - Searching param plugin for components ...
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.410] [DEBUG] - Search param plugin for oceanbase-ce
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.410] [DEBUG] - mkdir /home/admin/.obd/plugins
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.411] [DEBUG] - Found for oceanbase-ce-param-4.2.2.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.411] [DEBUG] - Applying oceanbase-ce-param-4.2.2.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-100000192024011915.el7-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.762] [DEBUG] - Search param plugin for obproxy-ce
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.763] [DEBUG] - Found for obproxy-ce-param-3.1.0 for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.763] [DEBUG] - Applying obproxy-ce-param-3.1.0 for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0-11.el7-0aed4b782120e4248b749f67be3d2cc82cdcb70d
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Searching connect plugin for components ...
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Searching connect plugin for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-100000192024011915.el7-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Found for oceanbase-ce-py_script_connect-4.2.2.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Searching connect plugin for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0-11.el7-0aed4b782120e4248b749f67be3d2cc82cdcb70d
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Found for obproxy-ce-py_script_connect-3.1.0 for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.846] [DEBUG] - Searching create_tenant plugin for components ...
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.847] [DEBUG] - Searching create_tenant plugin for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-100000192024011915.el7-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.847] [DEBUG] - Found for oceanbase-ce-py_script_create_tenant-4.2.0.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.847] [DEBUG] - Searching create_tenant plugin for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0-11.el7-0aed4b782120e4248b749f67be3d2cc82cdcb70d
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.847] [DEBUG] - No such create_tenant plugin for obproxy-ce-4.2.1.0
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.960] [INFO] Open ssh connection
[2024-02-19 19:09:04.960] [DEBUG] - host: 10.10.10.1, port: 22, user: admin, password: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.019] [DEBUG] - host: 10.10.10.2, port: 22, user: admin, password: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.076] [DEBUG] - host: 10.10.10.3, port: 22, user: admin, password: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.132] [DEBUG] - host: 10.10.10.2, port: 22, user: admin, password: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.221] [DEBUG] - Call oceanbase-ce-py_script_connect-4.2.2.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-100000192024011915.el7-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.221] [DEBUG] - import connect
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.281] [DEBUG] - add connect ref count to 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.282] [DEBUG] -- connect obshell (10.10.10.1:2886)
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.282] [DEBUG] -- connect obshell (10.10.10.2:2886)
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.282] [DEBUG] -- connect obshell (10.10.10.3:2886)
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.282] [INFO] Connect to observer
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.283] [DEBUG] -- connect 10.10.10.1 -P12881 -uroot -pRoot2023@@Root2023
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.284] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: select 1. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.414] [DEBUG] - sub connect ref count to 0
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.414] [DEBUG] - export connect
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.414] [DEBUG] - Call oceanbase-ce-py_script_create_tenant-4.2.0.0 for oceanbase-ce-4.2.2.0-100000192024011915.el7-aa3053da7370a6685a2ef457cd202d50e5ab75d3
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.414] [DEBUG] - import create_tenant
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.417] [DEBUG] - add create_tenant ref count to 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.418] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: select * from oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS where name like "test2_unit%" order by unit_config_id desc limit 1. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.420] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: select * from oceanbase.DBA_OB_TENANTS where TENANT_NAME = %s. args: ('test2',)
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.439] [INFO] Create tenant test2
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.440] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: select zone, count(*) num from oceanbase. __all_server where status = 'active' group by zone. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.441] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: select count(*) num from oceanbase. __all_server where status = 'active' and start_service_time > 0. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.442] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: SELECT * FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_SERVERS where zone in ('zone1','zone2','zone3'). args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.447] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: create resource unit test2_unit max_cpu 2.0, memory_size 2147483648, min_cpu 2.0, max_iops 10000, log_disk_size 3221225472. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.453] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: create resource pool test2_pool unit='test2_unit', unit_num=1, zone_list=('zone1','zone2','zone3'). args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:05.472] [DEBUG] -- execute sql: create tenant test2 replica_num=3,zone_list=('zone1','zone2','zone3'),primary_zone='RANDOM',resource_pool_list=('test2_pool'), charset = 'utf8'set ob_tcp_invited_nodes="%", ob_compatibility_mode = 'mysql'. args: None
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - sub create_tenant ref count to 0
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - export create_tenant
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [INFO] Trace ID: 4af55084-cf17-11ee-b825-00163e04608d
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [INFO] If you want to view detailed obd logs, please run: obd display-trace 4af55084-cf17-11ee-b825-00163e04608d
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - share lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo release, count 1
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - share lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo release, count 0
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - unlock /home/admin/.obd/lock/mirror_and_repo
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - exclusive lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/deploy_obtest release, count 0
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.645] [DEBUG] - unlock /home/admin/.obd/lock/deploy_obtest
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.646] [DEBUG] - share lock /home/admin/.obd/lock/global release, count 0
[2024-02-19 19:09:38.646] [DEBUG] - unlock /home/admin/.obd/lock/global
After the tenant is created, you can view it by running the following OBD command:
obd cluster tenant show obtest -t test2
The output is as follows:
Get local repositories and plugins ok
Get deployment connections ok
Connect to observer 10.10.10.1:2881 ok
Select tenant ok
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| tenant base info |
+-------------+-------------+--------------------+--------------+---------+---------+-------------+----------+----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+
| tenant_name | tenant_type | compatibility_mode | primary_zone | max_cpu | min_cpu | memory_size | max_iops | min_iops | log_disk_size | iops_weight | tenant_role |
+-------------+-------------+--------------------+--------------+---------+---------+-------------+----------+----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+
| test2 | USER | MYSQL | RANDOM | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0G | 10000 | 10000 | 3.0G | 0 | PRIMARY |
+-------------+-------------+--------------------+--------------+---------+---------+-------------+----------+----------+---------------+-------------+-------------+
Trace ID: 00f5e506-cf18-11ee-a74f-00163e04608d
If you want to view detailed obd logs, please run: obd display-trace 00f5e506-cf18-11ee-a74f-00163e04608d
Create a tenant by using SQL statements
Note
Log on as the root user to the sys tenant and execute the following statements.
The tenant creation procedure comprises three steps.
-
Create a unit config: This step is optional. If an appropriate unit config exists, you can skip this step and reuse the existing one.
-
Create a resource pool: You can either create a separate resource pool for each zone, allowing them to use independent unit configs, or create a single resource pool for all zones, so they share the same unit config.
-
Create a tenant: When you create a tenant, you must associate the tenant with the resource pool created in step 2.
(Optional) Step 1: Create a unit config
A unit config describes the specifications of each resource unit in a resource pool, such as the available CPU cores, memory, log disk size, and IOPS. After you create a unit config, resources are not actually allocated.
-
Create a unit config.
create resource unit u0 min_cpu=2,max_cpu=2,memory_size='2g', log_disk_size='6g',max_iops=10000; -
View the details of the unit config.
select * from oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS;The output is as follows. For more information about the
DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGSview, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS.+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
| UNIT_CONFIG_ID | NAME | CREATE_TIME | MODIFY_TIME | MAX_CPU | MIN_CPU | MEMORY_SIZE | LOG_DISK_SIZE | MAX_IOPS | MIN_IOPS | IOPS_WEIGHT |
+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
| 1 | sys_unit_config | 2024-02-19 15:33:47.524052 | 2024-02-19 15:33:47.524052 | 2 | 2 | 1073741824 | 3221225472 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 2 |
| 1001 | u0 | 2024-02-19 15:50:23.848604 | 2024-02-19 15:50:23.848604 | 2 | 2 | 2147483648 | 6442450944 | 10000 | 10000 | 0 |
+----------------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+---------+---------+-------------+---------------+---------------------+---------------------+-------------+
Step 2: Create a resource pool
When you create a resource pool, resource units are created. Resources are allocated to the resource units based on the unit config. If the resources reserved on a node are insufficient, the creation will fail. You can query the GV$OB_SERVERS view for the resource allocation information about all nodes. After a resource pool is created, you can query the DBA_OB_RESOURCE_POOLS and DBA_OB_UNITS views for the resource pool and its resource units.
Notice
A resource pool cannot be reused. After a tenant is created, the specified resource pool will be allocated to the tenant.
-
Create a resource pool.
create resource pool p1 unit='u0', zone_list=('zone1','zone2','zone3'),unit_num=1; -
Log on as the root user to the sys tenant of the OceanBase cluster and view the details of the resource pool.
select t4.tenant_id,t4.tenant_name,
t1.name resource_pool_name, t1.unit_count,
t2.`name` unit_config_name,
t2.max_cpu, t2.min_cpu,
ROUND(t2.memory_size/1024/1024/1024,2) mem_size_gb,
ROUND(t2.log_disk_size/1024/1024/1024,2) log_disk_size_gb, t2.max_iops,
t2.min_iops, t3.unit_id, t3.zone, concat(t3.svr_ip,':' ,t3.`svr_port`) observer
from oceanbase.dba_ob_resource_pools t1
join oceanbase.dba_ob_unit_configs t2 on (t1.unit_config_id=t2.unit_config_id)
join oceanbase.dba_ob_units t3 on (t1.`resource_pool_id` = t3.`resource_pool_id`)
left join oceanbase.dba_ob_tenants t4 on (t1.tenant_id=t4.tenant_id)
order by t4.tenant_name,t3.zone;The output is as follows:
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+-----------------+
| tenant_id | tenant_name | resource_pool_name | unit_count | unit_config_name | max_cpu | min_cpu | mem_size_gb | log_disk_size_gb | max_iops | min_iops | unit_id | zone | observer |
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+-----------------+
| NULL | NULL | p1 | 1 | u0 | 2 | 2 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 10000 | 10000 | 1007 | zone1 | 10.10.10.1:2882 |
| NULL | NULL | p1 | 1 | u0 | 2 | 2 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 10000 | 10000 | 1008 | zone2 | 10.10.10.2:2882 |
| NULL | NULL | p1 | 1 | u0 | 2 | 2 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 10000 | 10000 | 1009 | zone3 | 10.10.10.3:2882 |
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 1 | zone1 | 10.10.10.1:2882 |
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 2 | zone2 | 10.10.10.2:2882 |
| 1 | sys | sys_pool | 1 | sys_unit_config | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 9223372036854775807 | 9223372036854775807 | 3 | zone3 | 10.10.10.3:2882 |
+-----------+-------------+--------------------+------------+------------------+---------+---------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+-------+-----------------+Note
The newly created resource pool
p1is not associated with any tenant. Therefore, thetenant_idandtenant_namevalues in the output are bothNULL, meaning that the resource pool cannot be used by the business system.The following table describes the columns in the
DBA_OB_RESOURCE_POOLSview. For more information about the columns, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_RESOURCE_POOLS.Column Type Nullable Description NAME varchar(128) NO The name of the resource pool. UNIT_COUNT bigint(20) NO The number of resource units in the resource pool. The following table describes the columns in the
DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGSview. For more information about the columns, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNIT_CONFIGS.Column Type Nullable Description UNIT_CONFIG_ID bigint(20) NO The ID of the unit config. NAME varchar(128) NO The name of the unit config. MAX_CPU double NO The maximum number of CPU cores. MIN_CPU double NO The minimum number of CPU cores. MEMORY_SIZE bigint(20) NO The memory size, in bytes. LOG_DISK_SIZE bigint(20) NO The log disk size, in bytes. MAX_IOPS bigint(20) NO The maximum disk IOPS. MIN_IOPS bigint(20) NO The minimum disk IOPS. The following table describes the columns in the
DBA_OB_UNITSview. For more information about the columns, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_UNITS.Column Type Nullable Description UNIT_ID bigint(20) NO The ID of the resource unit. RESOURCE_POOL_ID bigint(20) NO The ID of the resource pool to which the resource unit belongs. ZONE varchar(128) NO The name of the zone. SVR_IP varchar(46) NO The IP address of the OBServer node to which the resource unit belongs. SVR_PORT bigint(20) NO The port number of the OBServer node to which the resource unit belongs. The following table describes the columns in the
DBA_OB_TENANTSview. For more information about the columns, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_TENANTS.Column Type Nullable Description TENANT_ID bigint(20) NO The ID of the tenant. Valid values: 1: the sys tenant.- Other values: a user tenant or meta tenant.
TENANT_NAME varchar(128) NO The name of the tenant. -
View the remaining available resources of the cluster.
SELECT ZONE,SVR_IP,SVR_PORT,
CPU_CAPACITY,CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX,CPU_CAPACITY-CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX as CPU_FREE,
ROUND(MEMORY_LIMIT/1024/1024/1024,2) as MEMORY_TOTAL_GB,
ROUND((MEMORY_LIMIT-MEM_CAPACITY)/1024/1024/1024,2) as SYSTEM_MEMORY_GB,
ROUND(MEM_ASSIGNED/1024/1024/1024,2) as MEM_ASSIGNED_GB,
ROUND((MEM_CAPACITY-MEM_ASSIGNED)/1024/1024/1024,2) as MEMORY_FREE_GB,
ROUND(LOG_DISK_CAPACITY/1024/1024/1024,2) as LOG_DISK_CAPACITY_GB,
ROUND(LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED/1024/1024/1024,2) as LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED_GB,
ROUND((LOG_DISK_CAPACITY-LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED)/1024/1024/1024,2) as LOG_DISK_FREE_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_CAPACITY/1024/1024/1024),2) as DATA_DISK_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_IN_USE/1024/1024/1024),2) as DATA_DISK_USED_GB,
ROUND((DATA_DISK_CAPACITY-DATA_DISK_IN_USE)/1024/1024/1024,2) as DATA_DISK_FREE_GB
FROM oceanbase.GV$OB_SERVERS;The output is as follows. After a resource pool is created, the available resources of the cluster become less. For more information about the
GV$OB_SERVERSview, see GV$OB_SERVERS.+-------+---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+----------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| ZONE | SVR_IP | SVR_PORT | CPU_CAPACITY | CPU_ASSIGNED_MAX | CPU_FREE | MEMORY_TOTAL_GB | SYSTEM_MEMORY_GB | MEM_ASSIGNED_GB | MEMORY_FREE_GB | LOG_DISK_CAPACITY_GB | LOG_DISK_ASSIGNED_GB | LOG_DISK_FREE_GB | DATA_DISK_GB | DATA_DISK_USED_GB | DATA_DISK_FREE_GB |
+-------+---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+----------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| zone2 | 10.10.10.2 | 2882 | 16 | 2 | 14 | 12.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 50.00 | 3.00 | 47.00 | 50.00 | 0.05 | 49.95 |
| zone1 | 10.10.10.1 | 2882 | 16 | 2 | 14 | 12.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 50.00 | 3.00 | 47.00 | 50.00 | 0.05 | 49.95 |
| zone3 | 10.10.10.3 | 2882 | 16 | 2 | 14 | 12.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 50.00 | 3.00 | 47.00 | 50.00 | 0.05 | 49.95 |
+-------+---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+----------+-----------------+------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------------+----------------------+------------------+--------------+-------------------+-------------------+
Step 3: Create a tenant
When you create a tenant, you can specify the RESOURCE_POOL_LIST parameter to allocate a resource pool to the tenant. You can either allocate a separate resource pool to each zone, allowing them to use independent unit configs, or allocate a single resource pool for all zones, so they share the same unit config. Besides RESOURCE_POOL_LIST, which is a required parameter, you can also set other important attributes and system variables such as the primary zone, locality, and connection allowlist.
CREATE TENANT IF NOT EXISTS test1 CHARSET='utf8mb4',
ZONE_LIST=('zone1','zone2','zone3'), PRIMARY_ZONE='RANDOM',
RESOURCE_POOL_LIST=('p1') SET ob_tcp_invited_nodes='%';
After tenant creation, you can query the DBA_OB_TENANTS view for all tenants.
SELECT * FROM oceanbase.DBA_OB_TENANTS \G
The output is as follows. For more information about the DBA_OB_TENANTS view, see oceanbase.DBA_OB_TENANTS.
*************************** 1. row ***************************
TENANT_ID: 1
TENANT_NAME: sys
TENANT_TYPE: SYS
CREATE_TIME: 2024-02-19 15:33:47.549569
MODIFY_TIME: 2024-02-19 15:33:47.549569
PRIMARY_ZONE: RANDOM
LOCALITY: FULL{1}@zone1, FULL{1}@zone2, FULL{1}@zone3
PREVIOUS_LOCALITY: NULL
COMPATIBILITY_MODE: MYSQL
STATUS: NORMAL
IN_RECYCLEBIN: NO
LOCKED: NO
TENANT_ROLE: PRIMARY
SWITCHOVER_STATUS: NORMAL
SWITCHOVER_EPOCH: 0
SYNC_SCN: NULL
REPLAYABLE_SCN: NULL
READABLE_SCN: NULL
RECOVERY_UNTIL_SCN: NULL
LOG_MODE: NOARCHIVELOG
ARBITRATION_SERVICE_STATUS: DISABLED
UNIT_NUM: 1
COMPATIBLE: 4.2.1.3
MAX_LS_ID: 1
*************************** 2. row ***************************
TENANT_ID: 1005
TENANT_NAME: META$1006
TENANT_TYPE: META
CREATE_TIME: 2024-02-19 19:03:03.358119
MODIFY_TIME: 2024-02-19 19:03:23.572876
PRIMARY_ZONE: RANDOM
LOCALITY: FULL{1}@zone1, FULL{1}@zone2, FULL{1}@zone3
PREVIOUS_LOCALITY: NULL
COMPATIBILITY_MODE: MYSQL
STATUS: NORMAL
IN_RECYCLEBIN: NO
LOCKED: NO
TENANT_ROLE: PRIMARY
SWITCHOVER_STATUS: NORMAL
SWITCHOVER_EPOCH: 0
SYNC_SCN: NULL
REPLAYABLE_SCN: NULL
READABLE_SCN: NULL
RECOVERY_UNTIL_SCN: NULL
LOG_MODE: NOARCHIVELOG
ARBITRATION_SERVICE_STATUS: DISABLED
UNIT_NUM: 1
COMPATIBLE: 4.2.1.3
MAX_LS_ID: 1
*************************** 3. row ***************************
TENANT_ID: 1006
TENANT_NAME: test1
TENANT_TYPE: USER
CREATE_TIME: 2024-02-19 19:03:03.360234
MODIFY_TIME: 2024-02-19 19:03:23.624946
PRIMARY_ZONE: RANDOM
LOCALITY: FULL{1}@zone1, FULL{1}@zone2, FULL{1}@zone3
PREVIOUS_LOCALITY: NULL
COMPATIBILITY_MODE: MYSQL
STATUS: NORMAL
IN_RECYCLEBIN: NO
LOCKED: NO
TENANT_ROLE: PRIMARY
SWITCHOVER_STATUS: NORMAL
SWITCHOVER_EPOCH: 0
SYNC_SCN: 1708340630218168002
REPLAYABLE_SCN: 1708340630218168002
READABLE_SCN: 1708340630218168001
RECOVERY_UNTIL_SCN: 4611686018427387903
LOG_MODE: NOARCHIVELOG
ARBITRATION_SERVICE_STATUS: DISABLED
UNIT_NUM: 1
COMPATIBLE: 4.2.1.3
MAX_LS_ID: 1003
3 rows in set (0.06 sec)
By default, the password of the administrator (root) of a newly created tenant is empty. We recommend that you set a password for the root user after tenant creation.
-
Generate a random string.
[admin@test001 ~]$ strings /dev/urandom |tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c8; echoThe output is as follows:
b******t -
Log on to OceanBase Database and set the random string as the password of the
rootuser.MySQL [oceanbase]> ALTER USER root IDENTIFIED BY 'b******t' ;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.118 sec)For more information about the
ALTER USERstatement, see ALTER USER.
Create a tenant by using ob-operator
Note
This section briefly describes how to create a tenant by using ob-operator. For more information, see Create a tenant.
Prerequisites
Before you create a tenant, make sure the following conditions are met:
-
The version of ob-operator is V2.1.0 or later.
-
You have deployed an OceanBase cluster, which is running normally.
Procedure
-
Create a configuration file.
For the content of the configuration file, see tenant.yaml in GitHub. For the detailed descriptions of the parameters in the configuration file, see Example.
-
Create a tenant.
Run the following command to create a tenant. This command creates an OBTenant resource for the tenant in the current Kubernetes cluster. In this example, the configuration file is named
tenant.yaml. Make sure to replace it with the actual file name.kubectl apply -f tenant.yaml -
Check whether the tenant is successfully created.
Run the following command to check whether the OBTenant resource of the newly created tenant is available in the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl describe obtenants.oceanbase.oceanbase.com -n oceanbase t1The output is as follows. The Status.status value of the OBTenant resource is
running. Related configurations are displayed in theStatussection.Name: t1
Namespace: oceanbase
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: oceanbase.oceanbase.com/v1alpha1
Kind: OBTenant
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2023-11-13T07:28:31Z
Finalizers:
finalizers.oceanbase.com.deleteobtenant
Generation: 2
Resource Version: 940236
UID: 34036a49-26bf-47cf-8201-444b3850aaa2
Spec:
Charset: utf8mb4
Connect White List: %
Credentials:
Root: t1-ro
Standby Ro: t1-ro
Force Delete: true
Obcluster: obcluster
Pools:
Priority: 1
Resource:
Iops Weight: 2
Log Disk Size: 12Gi
Max CPU: 1
Max Iops: 1024
Memory Size: 5Gi
Min CPU: 1
Min Iops: 1024
Type:
Is Active: true
Name: Full
Replica: 1
Zone: zone1
... # Some output information is omitted here.
Status:
Credentials:
Root: t1-ro
Standby Ro: t1-ro
Resource Pool:
Priority: 1
Type:
Is Active: true
Name: FULL
Replica: 1
Unit Config:
Iops Weight: 2
Log Disk Size: 12884901888
Max CPU: 1
Max Iops: 1024
Memory Size: 5368709120
Min CPU: 1
Min Iops: 1024
Unit Num: 1
Units:
Migrate:
Server IP:
Server Port: 0
Server IP: 10.10.10.1
Server Port: 2882
Status: ACTIVE
Unit Id: 1006
Zone List: zone1
... # Some output information is omitted here.
Status: running
Tenant Record Info:
Charset: utf8mb4
Connect White List: %
Locality: FULL{1}@zone1, FULL{1}@zone2, FULL{1}@zone3
Pool List: pool_t1_zone1,pool_t1_zone2,pool_t1_zone3
Primary Zone: zone3;zone1,zone2
Tenant ID: 1006
Unit Num: 1
Zone List: zone1,zone2,zone3
Tenant Role: PRIMARY
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal 2m58s obtenant-controller start creating
Normal 115s obtenant-controller create OBTenant successfully