Introduction
Keywords: resource pooling | manageability | cost reduction
OceanBase Database adopts a native multitenancy architecture, which supports multiple tenants in one cluster. Each tenant can be considered a database service. Data and resources of a tenant are isolated from those of other tenants, and tenant resources are uniformly scheduled within the cluster. Users can create MySQL tenants or Oracle tenants and configure the number, type, and storage location of data replicas as well as computing resources for each tenant.
SaaS Resource Consolidation
Microservice architecture
As the business system of an enterprise becomes more complex, a monolithic service architecture will cause overwhelming workload in engineering and management. If a microservice architecture is used, the enterprise can add and adjust services only by adding new microservice nodes. However, as each microservice needs a separate database, more services require more databases, leading to challenges for database reliability and O&M management.
With the multitenancy architecture of OceanBase Database, the administrator needs to maintain only a small number of clusters, with guaranteed isolation of tenant data and resources and improved database stability.
Multi-tenant SaaS
Generally, software-as-a-service (SaaS) cloud vendors provide multi-tenant services. If the spaces of multiple business tenants are logically isolated by tenant name in a single database, operations of different tenants can affect each other. If each business tenant uses a separate database, the large number of scattered databases can be a real headache for O&M engineers. The scalability is limited, let alone the high costs.
The native multitenancy architecture of OceanBase Database provides a better balance between resource isolation and costs, and tenants of any specification can be scaled in and out separately.
Current Status and Challenges of the Industry
-
Fragmented instances: Typically, a SaaS enterprise comprises multiple business applications or has to deploy many database instances to accommodate the resource isolation requirements of different customers. When the requests of a key business or customer surge, the performance and availability cannot be ensured because flexible scaling is not supported.
-
Resource waste: Due to fragmented deployment of database resources, a capacity margin is reserved for each instance to accommodate request growth within a short period. From the perspective of the whole business, the resource reservation is actually a great waste of resources, which increases the resource cost of the enterprise.
-
Complex management: The management efficiency for a large number of database instances is low. The database team cannot perform refined management on hundreds or thousands of instances. The time efficiency in recovery is low when events such as faults or jitters occur. The overall resource usage cannot be controlled globally, increasing the manual management cost.
Solution
OceanBase Database consolidates the database instances of different businesses based on its multitenancy architecture, improves the resource utilization, and ensures high availability for each resource unit by using the Paxos-based multi-replica mechanism.
OceanBase Database applies both to medium- and large-sized enterprises for resource pooling of different business links, and to SaaS vendors from different industries to provide instances of different specifications for different customers. This lowers the costs while ensuring resource isolation.
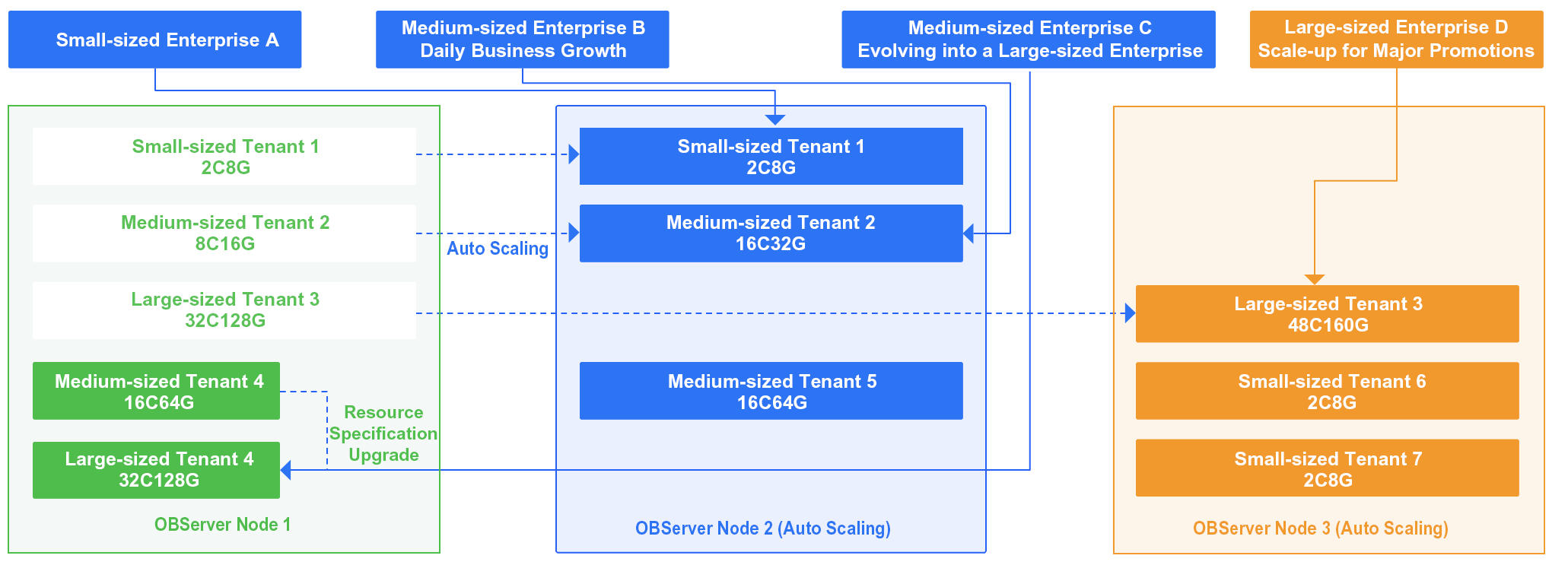
Solution Advantages
- Multi-tenant resource pooling: OceanBase Database natively supports resource isolation and virtualization for multiple tenants in the same cluster. This means that hundreds of database instances can be deployed in one OceanBase cluster. Data and resources are isolated for each tenant. Computing resources can be upgraded within seconds.
- Multidimensional scalability: The multi-node distributed architecture of OceanBase Database allows you to upgrade the specifications of an individual node, add more nodes to a cluster, and distribute the traffic across multiple nodes with higher specifications. The scaling is transparent to upper-layer applications. No manual intervention is required during the scaling for data migration. OceanBase Database automatically completes the data migration and multidimensional data verification.
- Unified management: After the scattered instances are deployed in OceanBase Database in a unified manner, the complexity in O&M management is significantly reduced. Before the optimization, the database administrator (DBA) needs to manage hundreds of scattered instances. After the optimization, the DBA needs to manage only a couple of OceanBase clusters. Loads, alerts, and tuning are all consolidated to the cluster level. Common faults can be automatically troubleshot, significantly improving the business support efficiency and emergency response capability.
- Cost reduction and efficiency improvement: Computing resources are pooled based on the multitenancy architecture, improving the overall resource utilization. The advanced compression feature of OceanBase Database reduces the storage cost by 2/3 compared to a conventional database. According to extensive feedback from customers and statistics of cases, the resource consolidation solution of OceanBase Database can help medium- and large-sized enterprises reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) by about 30% to 50%.
Cases
Dmall
Business challenges
Dmall markets its services across borders. In China, its customers include large supermarkets, such as Wumart and Zhongbai, as well as multinational retailers, such as METRO AG and 7-Eleven. Dmall also serves many Chinese and international brands. It links brand owners, suppliers, and retailers with smooth data and information flows so that they can better support and serve consumers. The long service chain, from manufacturers, brand owners, and suppliers, to retailers in various shopping malls and stores, and finally to consumers, generates massive data volumes. The system complexity increases exponentially with the data volume. As a result, the retail SaaS system of Dmall faces three major challenges:
- Complex O&M: Dmall uses a microservice architecture that involves many business links in the overall process and a large system application scale. Dmall already has more than 500 databases. Moreover, as its system continues to iterate, the data scale continues to increase, and O&M management is becoming more and more difficult.
- Rapid business growth and more horizontal scaling requirements: Dmall formulated a global expansion strategy to cope with its business growth. According to the requirements of regional data security laws, it needs to deploy a new system to undertake business traffic outside China. It is hard to predict future business scale and data growth in the initial deployment phase. Therefore, database resource allocation in the initial deployment phase is quite difficult. The common practice is to deploy the system with limited resources at low costs. However, rapid business growth and exponential data increase will require quick scaling.
- Serving a large number of merchants in the same cluster: The number of stock keeping units (SKUs) of different convenience stores and supermarket chains ranges from thousands to tens of thousands. Therefore, it is impossible for Dmall to deploy an independent system for each customer. This means that Dmall SaaS system must support hundreds of small and medium-sized business customers, and the data generated by all merchants shares database resources at the underlying layer. Moreover, Dmall has massive individual tenants in the system, such as large chain stores. It wants to isolate the resources for these tenants from those for others.
Solution
- OceanBase Database consolidates multiple individual instances in one OceanBase cluster for unified management and flexible scheduling, thereby effectively improving the resource utilization.
- Resources are isolated based on tenants. The data of different business modules is isolated from each other. Specifications are transparently upgraded or downgraded as needed.
- With the powerful intelligent management platform of OceanBase Database, typical faults are automatically detected and analyzed, significantly improving the O&M efficiency.
- OceanBase Migration Service (OMS) is used to efficiently migrate all business data to OceanBase Database with slight or zero business reconstruction.
- Based on the powerful leader distribution and read/write routing strategies of OceanBase Database, Ant Group's high-concurrency best practices accumulated over years are shared with customers.
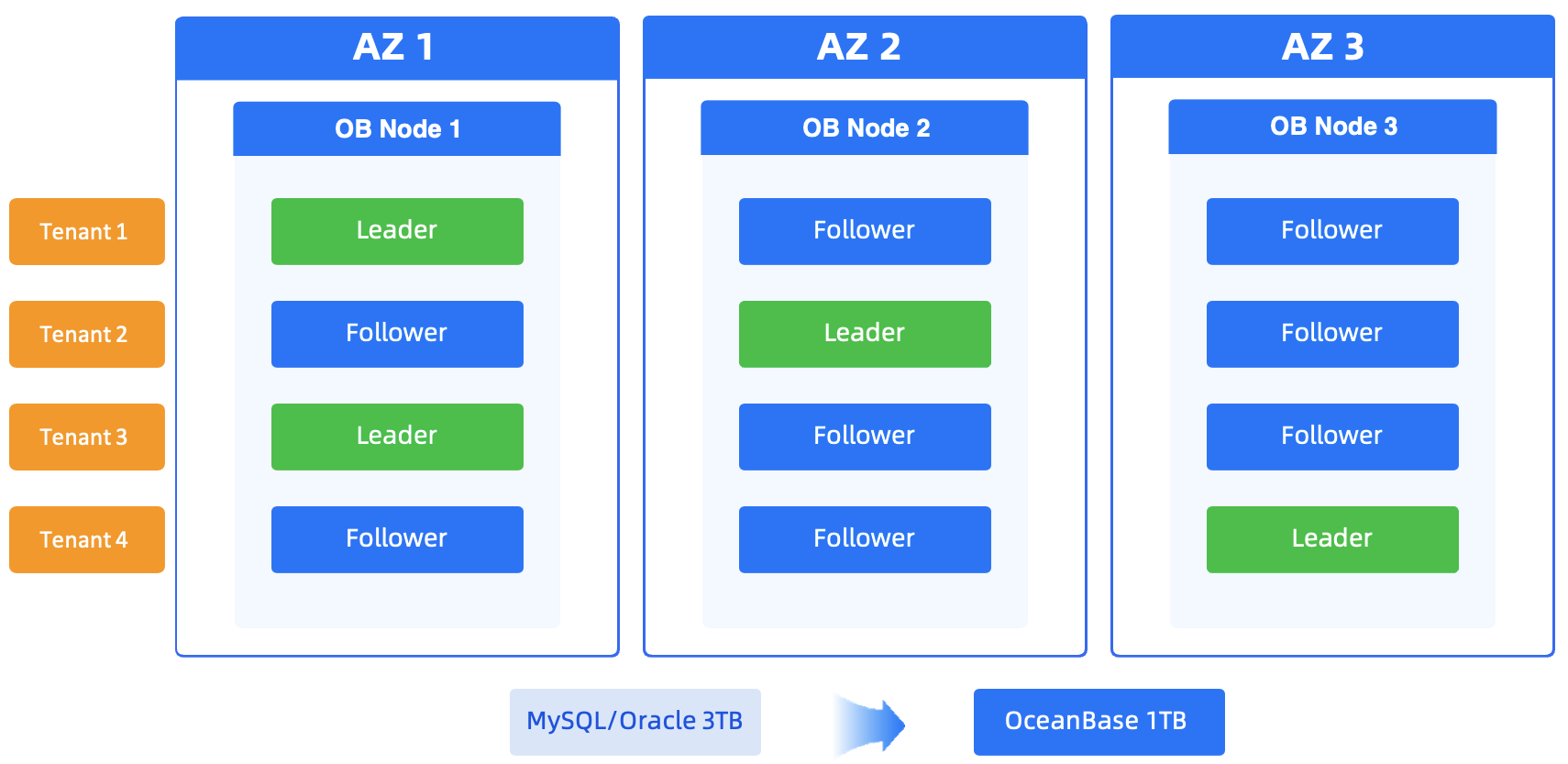
Customer benefits
- In a multi-tenant cluster, resources can be scaled for a database instance within seconds to support business peaks without adjusting the overall resources of the cluster.
- OceanBase Database effectively reduces the O&M cost and error probability while addressing the issue of business scalability. In terms of Internet Data Center (IDC)-level disaster recovery, OceanBase Database achieves a recovery point objective (RPO) of 0 and a recovery time objective (RTO) of less than 8s. It can support hundreds of millions of users.
- With the advanced compression technology, OceanBase Database saves the data storage space by nearly 6 times while ensuring the performance. In other words, OceanBase Database can store more data by using the same hardware resources.
- OceanBase Database is highly compatible with the SQL statements, stored procedures, and triggers of MySQL. Existing business data can be smoothly migrated to OceanBase Database without business interruption.
Other cases
- E-surfing Pay: https://open.oceanbase.com/blog/4446837760
- Industry: government enterprises and network operators
- Pain points: E-surfing Pay deployed multiple databases in a database cluster, with resources shared among them. When any database was experiencing traffic surges during peak hours, the services of other databases were affected, which significantly impacted the user experience.
- Benefits: OceanBase Database supports multitenancy and resource isolation. E-surfing Pay needs to deploy multiple databases for some business modules, such as the online mall. To avoid resource contention among these databases, which may affect other business modules, each database is contained in an OceanBase Database tenant. Resources for each tenant are isolated, so that we can limit the amount of resources for each database. Furthermore, the amount of tenant resources can be adjusted as needed, which means E-surfing Pay can adjust resources of each database. This ensures the business stability and flexibility.
- China Unicom: https://open.oceanbase.com/blog/8185228352
- Industry: government enterprises and network operators
- Pain points: A large number of scattered databases was a real headache for O&M engineers, and the scalability was limited.
- Benefits: OceanBase Database supports multiple tenants in one cluster. Each tenant provides services as a database. Data and resources of a tenant are isolated from those of other tenants, and tenant resources are uniformly scheduled within the cluster.
- TAL: https://open.oceanbase.com/blog/7832546560
- Industry: education
- Pain points: The original database was deployed in standalone mode with multiple instances. It did not support resource isolation and generated a large number of resource fragments. The resource deployment mode did not support scaling. A large resource margin was reserved during allocation, leading to low resource utilization.
- Benefits: OceanBase Database implements resource isolation and scaling based on its multitenancy architecture. Furthermore, extra cost benefits are gained through data compression.
- Sunshine Insurance: https://open.oceanbase.com/blog/8657676560
- Industry: financing
- Pain points: The original MySQL database hosted many small business modules, leading to complex O&M.
- Benefits: OceanBase Database implements resource isolation based on its multitenancy architecture. Resources are allocated based on business needs, maximizing the use of server resources.
- KEYTOP: https://open.oceanbase.com/blog/7521893152
- Industry: logistics and mobility service
- Pain points: The SaaS architecture of the entire platform failed to be upgraded based on the original MySQL database. All groups ran independently without data interactions. Some groups demanded data isolation. SaaS can reduce a part of the private deployment and O&M costs.
- Benefits: OceanBase Database simplifies private deployment and operations. Based on the group scale, tenants of different specifications are selected to more clearly calculate the resources used by each group and estimate the expenses. After resource isolation, the data amount of each group will be smaller than that of all groups aggregated together. This way, the system can achieve higher performance, stability, and scalability.