Inter K8s cluster management
This feature is available in ob-operator version 2.3.0 and later. Prerequisite: Pod and service connectivity must be established across all K8s clusters involved.
Deploying workloads across multiple K8s clusters enhances scalability, reliability, and security. By deploying zones (obzones) across different K8s clusters, you can fully leverage OceanBase's high-availability design. This approach provides disaster tolerance at the K8s cluster level, making operations more resilient.
Architecture
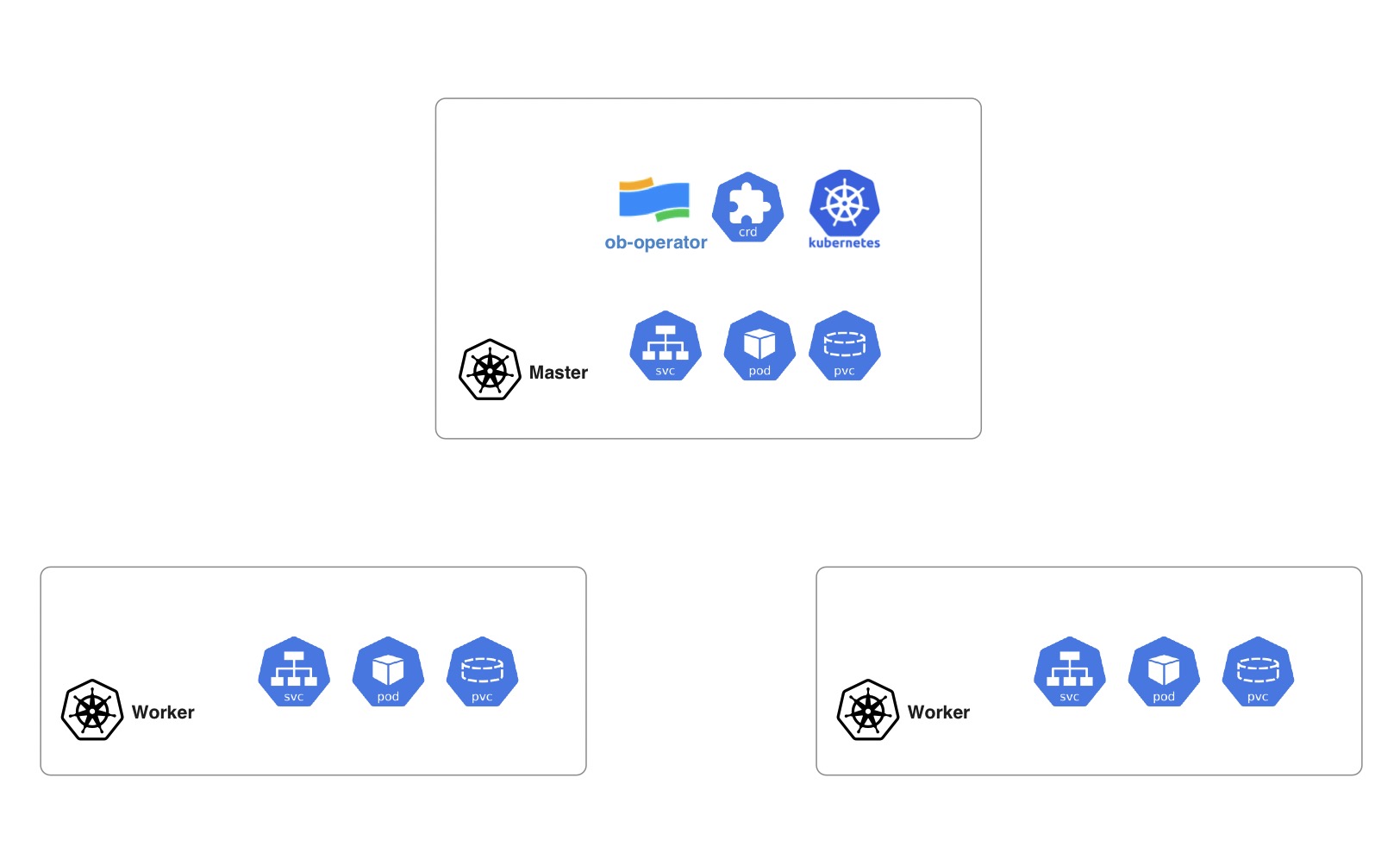
As shown in the architecture diagram, K8s clusters play different roles. The cluster running the ob-operator is referred to as the master cluster, while the other clusters are called worker clusters. Worker clusters are registered by creating a custom resource of type K8sCluster in the master cluster. The ob-operator accesses these worker clusters using credentials stored in these resources. While OceanBase workloads run as native K8s resources in the worker clusters, the custom resources for OceanBase remain in the master cluster.
How to add worker K8s Cluster
To add a worker cluster, ensure the credentials used for access have permissions to get, list, watch, create, update, patch and delete resources of type pod, service, pvc, job and namespace. Follow the example below to create a K8sCluster resource by replacing the placeholder under kubeConfig with your worker cluster’s credentials, then apply it to the master cluster.
apiVersion: k8s.oceanbase.com/v1alpha1
kind: K8sCluster
metadata:
name: k8s-remote
spec:
name: remote
description: "This is the remote k8s cluster for testing"
kubeConfig: |
<Your K8s credential> # Typically you can found it in ~/.kube/config
Verify the resource using the following command
kubectl get k8scluster
The expected output should look like this
NAME AGE CLUSTERNAME
k8s-remote 1m remote
Create OceanBase Cluster across multiple K8s clusters
To create an OceanBase cluster across multiple K8s clusters, the only difference compared with deploy it in a single K8s cluster is to specify in which K8s cluster the obzone should be created, you may reference the following example.
apiVersion: oceanbase.oceanbase.com/v1alpha1
kind: OBCluster
metadata:
name: test
namespace: default
# annotations:
# "oceanbase.oceanbase.com/independent-pvc-lifecycle": "true"
# "oceanbase.oceanbase.com/mode": "service"
spec:
clusterName: test
clusterId: 1
userSecrets:
root: root-password
topology:
- zone: zone1
replica: 1
- zone: zone2
replica: 1
k8sCluster: k8s-cluster-hz
- zone: zone3
replica: 1
k8sCluster: k8s-cluster-sh
observer:
image: oceanbase/oceanbase-cloud-native:4.2.1.7-107000162024060611
resource:
cpu: 2
memory: 10Gi
storage:
dataStorage:
storageClass: local-path
size: 50Gi
redoLogStorage:
storageClass: local-path
size: 50Gi
logStorage:
storageClass: local-path
size: 20Gi
parameters:
- name: system_memory
value: 1G
- name: "__min_full_resource_pool_memory"
value: "2147483648" # 2G
Managing OceanBase Cluster in multiple K8s clusters
Managing an OceanBase cluster across multiple K8s clusters remains straightforward. Simply modify the custom resources in the master cluster, and the ob-operator will synchronize the changes with the relevant resources in the worker clusters.